Breadcrumb
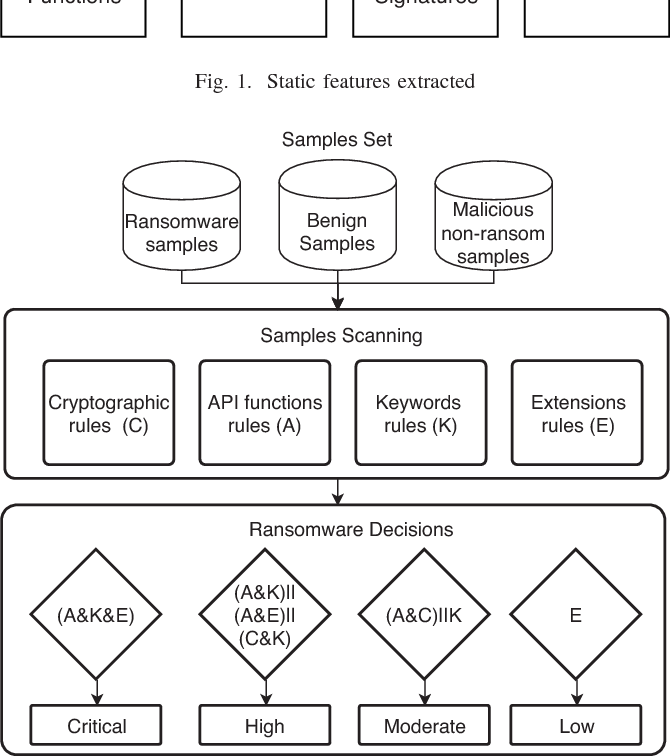
A new static-based framework for ransomware detection
Recently, ransomware attacks are on the rise hitting critical infrastructures and organizations globally. Ransomware uses advanced encryption techniques to encrypt important files on the targeted computer, then it requests payment to decrypt the encrypted files again. Therefore, the detection and prevention of ransomware attacks represent major challenges for security researchers. This research proposes a novel static-based rules ransomware detection framework. The decision rules of the proposed framework are based on static features extracted from the ransomware files. When scanned file
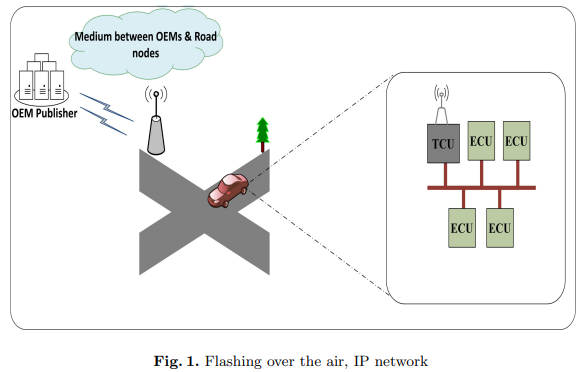
Vehicle Software Update over ICN Architectures
The Internet Protocol (IP) architecture could not fully satisfy Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) needed efficiency due to their dynamic topology and high mobility. This paper presents a technique to update the software of Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in vehicles using Information Centric Network (ICN) architecture. The proposed technique replaces Flashing Over The Air (FOTA) using IP with FOTA using ICN. The importance of FOTA is illustrated as well as the impact of applying the ICN architecture on VANETs. Through our experiments, we compare between the known FOTA over IP and the newly
Decoding arm kinematics from EMG signals using Kalman filter
Myoelectric control of prosthetic arms provides a new hope for providing naturalistic movements to amputees. Extensive work has been made in recent years to use Electromyography (EMG) signals to enhance the operation of prosthetic arms. In this paper, we propose an EMG Kalman filter-based model, where we identify the relationship between the joint angles and recorded EMG signals. EMG signals were recorded from biceps and triceps muscles and used to train a Kalman filter decoder. We assessed the performance of the decoder by computing the correlation and the normalized root mean-square error
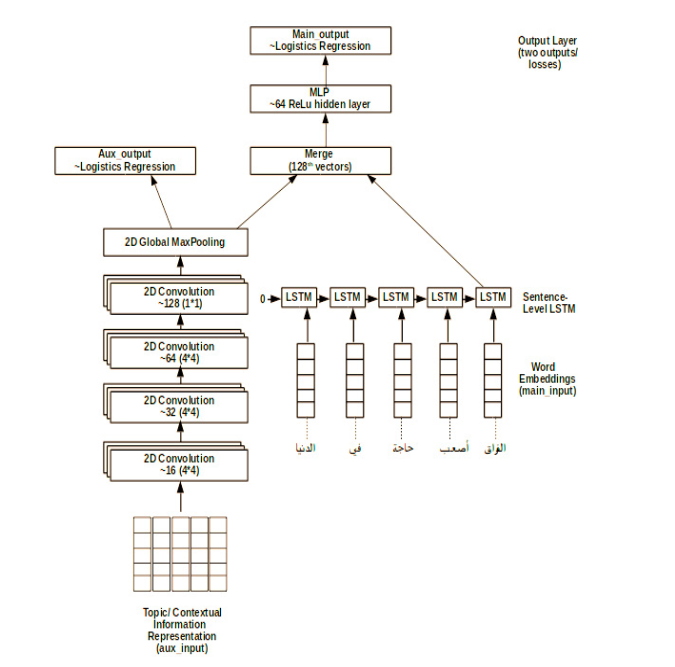
A Context Integrated Model for Multi-label Emotion Detection
This paper explores the impact of taking the environment within which a tweet is made, on the task of analyzing sentiment orientations of tweets produced by people in the same community. The paper proposes C-GRU (Context-aware Gated Recurrent Units), which extracts the contextual information (topics) from tweets and uses them as an extra layer to determine sentiments conveyed by the tweet. The proposed architecture learns direct co-relations between such information and the task's predication. The multi-modal model combines both outputs learnt (from topics and sentences) by learning the
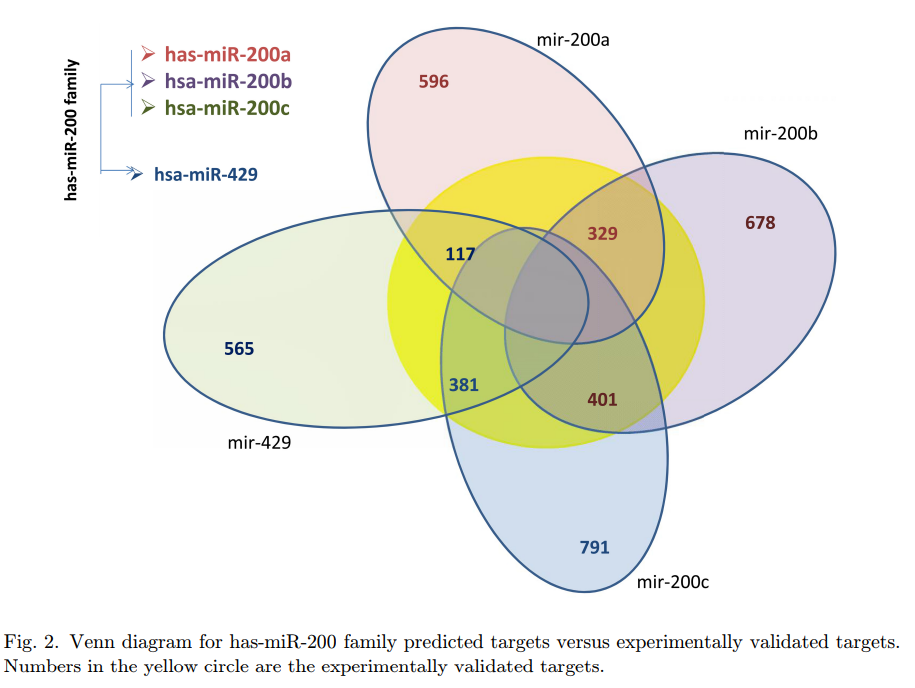
MicroTarget: MicroRNA target gene prediction approach with application to breast cancer
MicroRNAs are known to play an essential role in gene regulation in plants and animals. The standard method for understanding microRNA-gene interactions is randomized controlled perturbation experiments. These experiments are costly and time consuming. Therefore, use of computational methods is essential. Currently, several computational methods have been developed to discover microRNA target genes. However, these methods have limitations based on the features that are used for prediction. The commonly used features are complementarity to the seed region of the microRNA, site accessibility
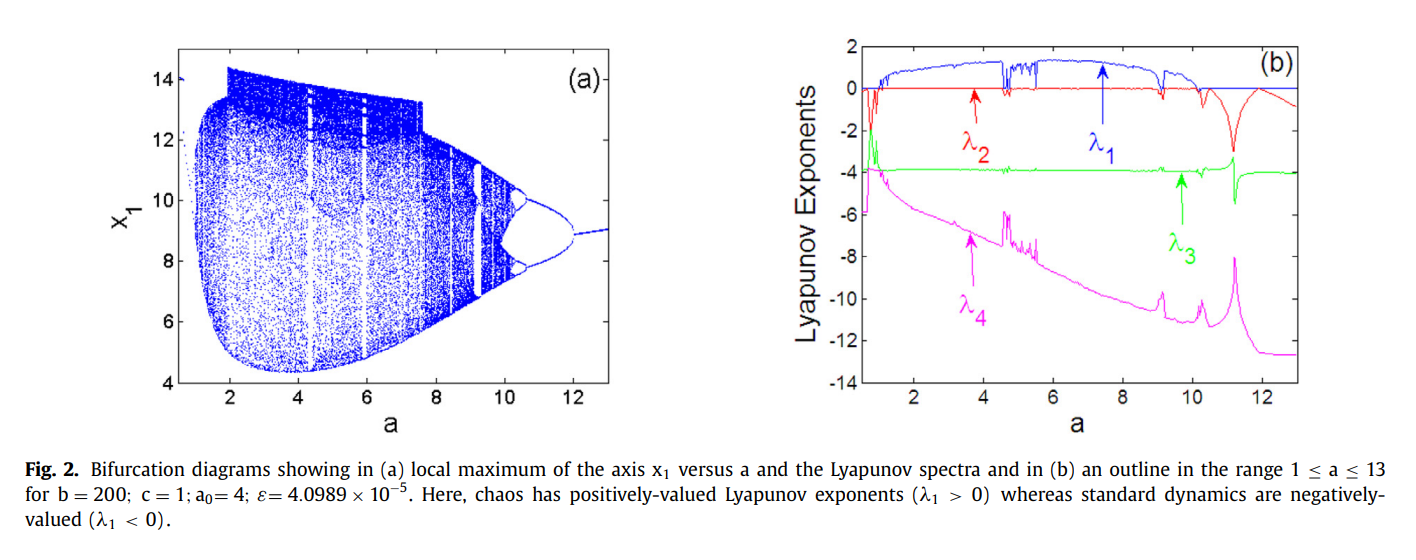
Design and implementation of a simple dynamical 4-D chaotic circuit with applications in image encryption
We present a simple yet highly dimensional hybrid diode bridge circuit network that can exhibit complex chaotic behaviours. Further, since our network is characterised by smooth fourth-order exponential nonlinearity, we employ a distinctive approach to assess its different properties: we examine the circuit stability near fixed points. Specifically, we evaluate dynamic complexity using the Lyaponov spectrum analysis, bifurcation analysis and phase space trajectories; additionally, we assess coexisting attractors in the parameter space using numerical and experimental analysis. Furthermore, we
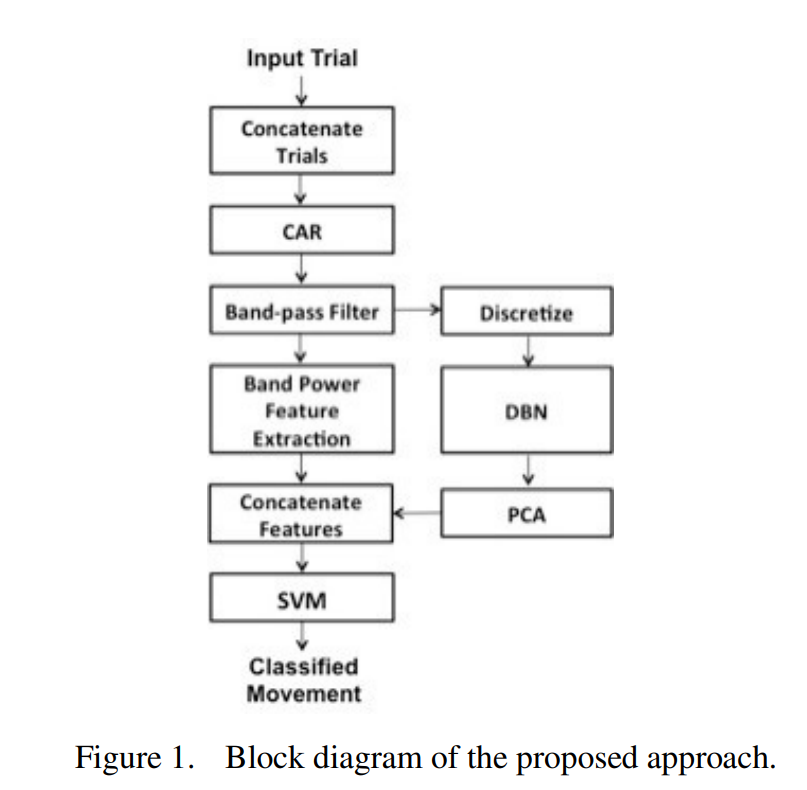
Dynamic Bayesian Networks for EEG motor imagery feature extraction
Dynamic Bayesian Networks (DBNs) are efficient graphical tools that could be used to detect causal relationships in multivariate systems. Here, we utilize DBNs to infer causality among electroencephalography (EEG) electrodes during a motor imagery task. We inferred the causal relationships between EEG electrodes during each of right and left hands imagery movements from 9 different subjects. We demonstrate how using the inferred connectivity as a feature enhances the discrimination among right and left hands imagery movements compared to using traditional band power features. Our analysis
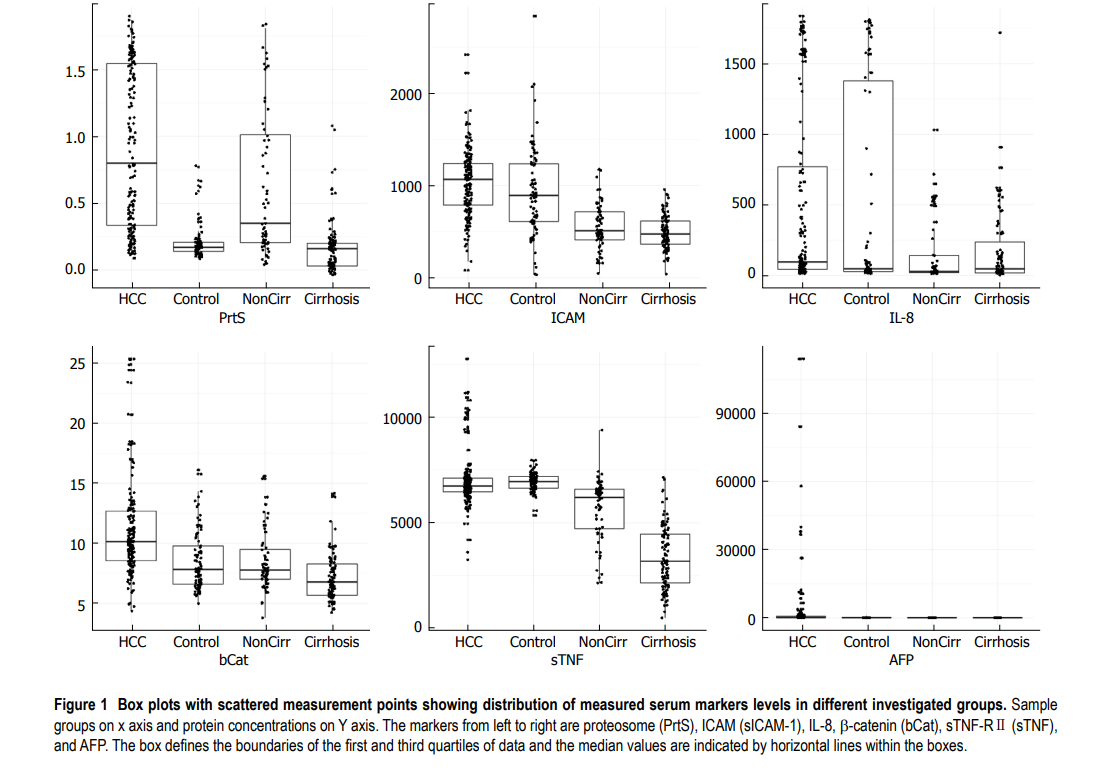
Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma co-occurring with hepatitis C virus infection: A mathematical model
AIM: To develop a mathematical model for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with a panel of serum proteins in combination with α-fetoprotein (AFP). METHODS: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-8, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor II (sTNF-R II), proteasome, and β-catenin were measured in 479 subjects categorized into four groups: (1) HCC concurrent with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (n = 192); (2) HCV related liver cirrhosis (LC) (n = 96); (3) Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) (n = 96); and (4) Healthy controls (n = 95). The

Machine learning methodologies in Brain-Computer Interface systems
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a one kind of communication system that enables control of devices or communication with others only through brain signal activities without using motor activities. The main application for BCI is to provide an alternative channel for helping disabled persons, hereafter mentioned as subjects, to communicate with the external world. This paper tries to demonstrate the performance of different machine learning algorithms based on classification accuracy. Performance has been evaluated on dataset II from BCI Competition III for the year 2004 for two subjects 'A'
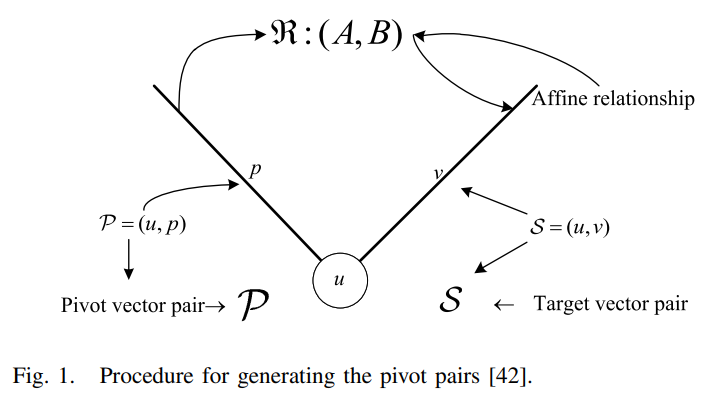
Dominant Data Set Selection Algorithms for Electricity Consumption Time-Series Data Analysis Based on Affine Transformation
In the explosive growth of time-series data (TSD), the scale of TSD suggests that the scale and capability of many Internet of Things (IoT)-based applications has already been exceeded. Moreover, redundancy persists in TSD due to the correlation between information acquired via different sources. In this article, we propose a cohort of dominant data set selection algorithms for electricity consumption TSD with a focus on discriminating the dominant data set that is a small data set but capable of representing the kernel information carried by TSD with an arbitrarily small error rate less than
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 18
- Next page ››
