Breadcrumb
Frational Order Inverse Filters Based on CCII Family
This paper proposes two generalized topologies of fractional order inverse filters (FOIF). All possible realizations of each topology are investigated using the second generation current conveyor (CCII) family. Inverse fractional highpass (IFHPF), inverse fractional bandpass (IFBPF), and inverse fractional lowpass (IFLPF) filters are realized using the same topology based on the generalized admittances. Numerical and P-Spice simulation results are presented for selected cases to approve the theoretical findings. The fractional order parameters increase the design flexibility and

Capacitive behavior and stored energy in supercapacitors at power line frequencies
Supercapacitors are commonly viewed and mainly employed as dc electrical energy storage devices. Their behavior at far-from-dc is usually overlooked and not well explored for potential applications. In this work, we investigate analytically and experimentally the performance of supercapacitor at high frequencies, including the 50 Hz/60 Hz power line frequencies. The variation of effective capacitance, power and energy with frequency are analyzed using a fractional-order model consisting of a series resistance and a constant phase element for both pure sinusoidal and full-wave rectified voltage
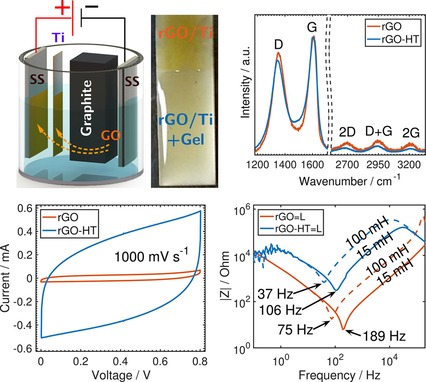
All-Solid-State Double-Layer Capacitors Using Binderless Reduced Graphene Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Bipolar Electrochemistry
Bipolar electrochemistry is used as an economical, single-step, and scalable process for the oxidation of a wireless graphite substrate, and the subsequent electrophoretic deposition of graphene oxide thin film on a second wireless substrate. An all-solid-state symmetric double-layer capacitor (EDLC) using binderless reduced graphene oxide electrodes exhibited outstanding reversibility and capacitance retention over 18000 cycles, as well as superior capacitive behavior at far-from-dc frequencies (for example 45 and 47 µ F cm-2), effective capacitances at 75 and 189 Hz, respectively (computed
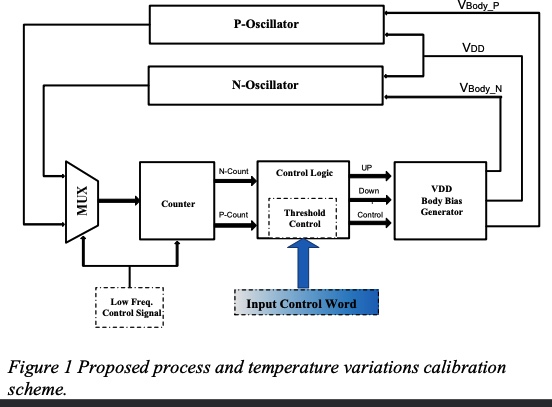
A dynamic power-aware process variation calibration scheme
In this paper, a power-aware process variation calibration scheme is proposed. The proposed calibration system provides the ability to detect and control the n- and p-type variations independently through the use of all-n and all-p ring oscillators. Calibration is then carried out through the use of the supply voltage and body bias to alter the device parameters to match those of a certain process corner that is determined by the system designer. This scheme is characterized by its ability to dynamically change the desired mapping target according to the computational load. The calibration
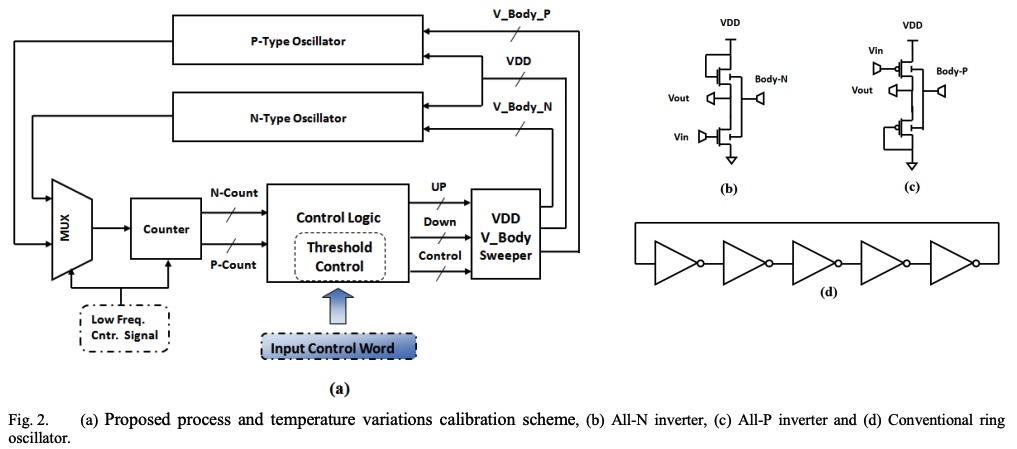
A dynamic calibration scheme for on-chip process and temperature variations
A process and temperature variation calibration scheme is proposed in this paper. The proposed system uses the supply voltage and body bias to calibrate the device parameters to match those of a certain process corner that is determined by the system designer. This scheme is characterized by its ability to dynamically change the desired mapping target according to the computational load. Moreover, the proposed system provides the ability to detect and control the n- and p-type variations independently through the use of an all-n and all-p ring oscillators. The calibration system has been
Resonant square-wave clock generator for low power applications
Power reduction is the main challenge facing circuit designers in their quest to utilize the full performance of new process technologies. A major portion of the power consumed in today's systems is due to the clock generation and distribution. Resonant clocking has been a promising technique to reduce the clock power dramatically. In this paper, a novel resonant clock generator circuit is proposed to reduce the dynamic power used for clock generation by almost 75%. Two configurations of the circuit are presented. The merit of this generator is most obvious in the ease of its implementation
Communication—convolution-based estimation of supercapacitor parameters under periodic voltage excitations
Supercapacitors are typically used in applications requiring frequent and continuous charging/discharging cycles, but most of the models available in the literature are designed to predict their behavior for a single sequence. In this letter, we show first that the electrical response and metrics of supercapacitors under periodic voltage excitations can generally be obtained using Fourier series analysis and convolution operations of functions derived based on any suitable impedance model. We verified our analysis procedure with simulations using particle swarm optimization, and experiments
Communication-The Ragone Plot of Supercapacitors under Different Loading Conditions
The power-energy performance of supercapacitors is usually visualized by the Ragone plot of (gravimetric or volumetric) energy density vs power density. The energy is commonly computed from E = CV2/2, and the power from P = E/Δt, which assume RCbased models. In this study, we investigate the energy-power profiles of two commercial supercapacitors discharged with three different types of loads: (i) constant current, (ii) constant power, and (iii) constant resistive load. The energy is computed as per the definition from the time-integral of its instantaneous power, i.e. E(t) = ò p(t)dt with p(t

Investigation of properties limiting efficiency in Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
We have investigated different nonidealities in Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with 9.7% conversion efficiency, in order to determine what is limiting the efficiency of these devices. Several nonidealities could be observed. A barrier of about 300 meV is present for electron flow at the absorber-buffer heterojunction leading to a strong crossover behavior between dark and illuminated current-voltage curves. In addition, a barrier of about 130 meV is present at the Mo-absorber contact, which could be reduced to 15 meV by inclusion of a TiN interlayer. Admittance spectroscopy results on the
Hierarchical proactive caching for vehicular ad hoc networks
Recently, emerging vehicular applications are increasing the demand of vehicles which form significant burdens on network backhaul and represents a cause to the quality of experience (QoE) decay of the vehicular users. Proactive caching is a promising technique to mitigate the load on core networks by caching some of the expected data items. This work proposes a hierarchical proactive caching scheme which jointly considers caching in vehicles and roadside units (RSUs). Minimization of the vehicle communication latency is the main objective of our study. The optimization problem is formulated
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
