Breadcrumb
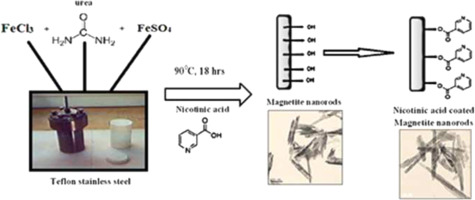
Synthesis of non-aggregated nicotinic acid coated magnetite nanorods via hydrothermal technique
Non-aggregated magnetite nanorods with average diameters of 20-30 nm and lengths of up to 350 nm were synthesized via in situ, template free hydrothermal technique. These nanorods capped with different concentrations (1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 g) of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3); possessed good magnetic properties and easy dispersion in aqueous solutions. Our new synthesis technique maintained the uniform shape of the nanorods even with increasing the coating material concentration. The effect of nicotinic acid on the shape, particle size, chemical structure and magnetic properties of the prepared
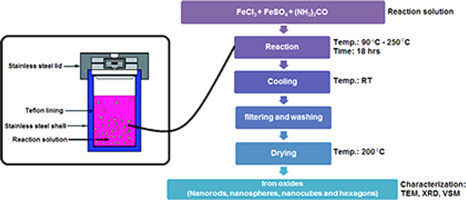
Tailored super magnetic nanoparticles synthesized via template free hydrothermal technique
Magnetite nanoparticles of controlled shape and dimensions were synthesized using a modified hydrothermal technique. The influence of different synthesis conditions on the shape, size (length and diameter), structure and magnetic properties of the prepared nanoparticles is presented. The mineral phases, the morphologies, size distribution of the resulting magnetic nanoparticles and their magnetic properties were characterized using different characterization methods. We designed magnetite nanoparticles with different morphologies (nanospheres, nanorods, nanocubes and hexagons) and with
Synthesis of CuO-distributed carbon nanofiber: Alternative hybrid for solid propellants
Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) possess superior catalytic abilities and high surface area. Moreover, energetic particles can be loaded on them by acting as carriers. The current study reports an electroless plating, effective deposition of copper particles (Cu) on the surface of CNFs. The prepared Cu–CNFs hybrid was annealed at 250 °C to form CuO–CNFs. Homogeneous loading of CuO particles on CNFs was revealed via TEM analysis, while the crystalline structure was studied using XRD analysis. In addition, ammonium perchlorate (AP) oxidizer with endothermic initial decomposition was mixed with the
The economic potential of using cotton stalks to produce alternative wooden materials
The wooden industry depends heavily on logging activities which have negative impacts on the environment and a shortage of supply. The industry is starting to depend on composite boards from agricultural waste materials. Composite boards have been shown in the literature. However, some wooden applications still depend on hardwoods. Besides, most of these composite boards use synthetic formaldehyde as binders. Formaldehydes have negative impacts on human health. On the other hand, Egypt has an abundance of cotton waste that can produce composite woods. In this paper, the researchers compared
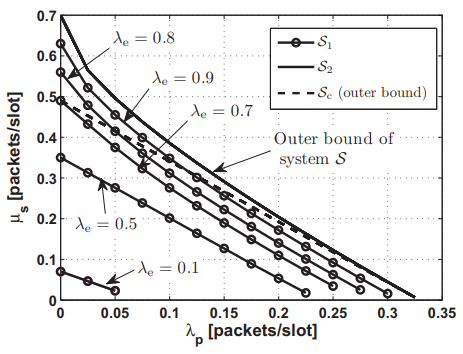
Maximum throughput of a cooperative energy harvesting cognitive radio user
In this paper, we investigate the maximum throughput of a saturated rechargeable secondary user (SU) sharing the spectrum with a primary user (PU). The SU harvests energy packets (tokens) from the environment with a certain harvesting rate. All transmitters are assumed to have data buffers. In addition to its own traffic buffer, the SU has a buffer for storing the admitted primary packets for relaying; and a buffer for storing the energy tokens harvested from the environment. We propose a new cooperative cognitive relaying protocol that allows the SU to relay a fraction of the undelivered
Chitosan/carbon nanotube composite beads: Preparation, characterization, and cost evaluation for mercury removal from wastewater of some industrial cities in Egypt
Composite beads composed of chitosan (CS) with different carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were prepared by the incorporation of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOHs). A protected crosslinking method was used for the preparation of the CS/CNTs beads by the reaction of the beads with Hg(II) as the protector. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis were used to characterize the prepared beads. The adsorption performance of the prepared beads was
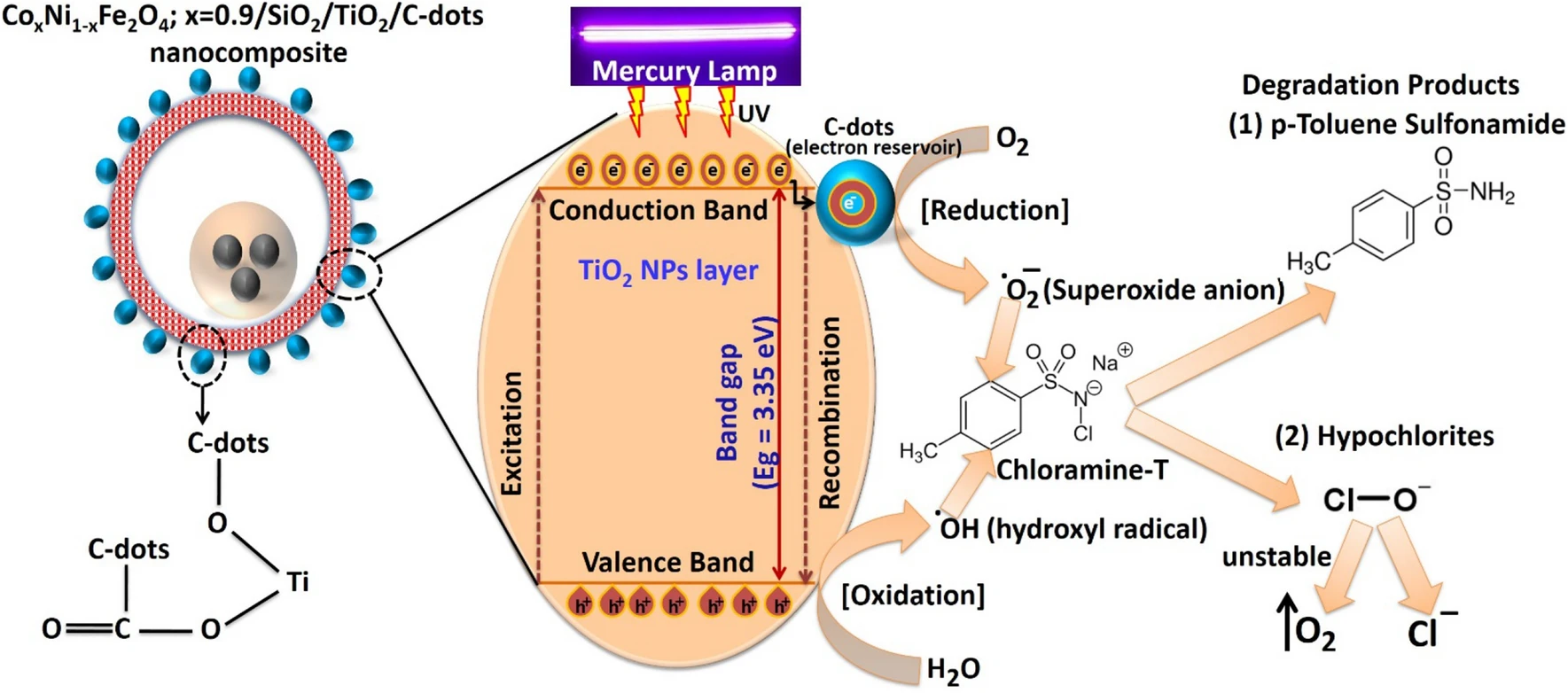
Carbon-dot-loaded CoxNi1−xFe2O4; x = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial potential: An engineered nanocomposite for wastewater treatment
Water scarcity is now a serious global issue resulting from population growth, water decrease, and pollution. Traditional wastewater treatment plants are insufficient and cannot meet the basic standards of water quality at reasonable cost or processing time. In this paper we report the preparation, characterization and multiple applications of an efficient photocatalytic nanocomposite (CoxNi1−xFe2O4; x = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2/C-dots) synthesized by a layer-by-layer method. Then, the photocatalytic capabilities of the synthesized nanocomposite were extensively-studied against aqueous solutions of
Combined effect of wind speed and covering irrigation canals on water quality parameters
Wind has a considerable effect on many water quality parameters. Some of the parameters are directly affected by the wind, while others are influenced by other physical water parameters like the velocity, temperature. etc.That are affected by wind and hence transfer their effect to water quality parameters. As the wind has an effect on water quality parameters, also covering waterways has a great effect on the water quality of those covered waterways. This is because covering a waterway alters the concentrations of its water quality parameters. This research is concerned with studying the
Combined effect of wind speed and covering irrigation canals on water quality parameters
Wind has a considerable effect on many water quality parameters. Some of the parameters are directly affected by the wind, while others are influenced by other physical water parameters like the velocity, temperature. etc. that are affected by wind and hence transfer their effect to water quality parameters. As the wind has an effect on water quality parameters, also covering waterways has a great effect on the water quality of those covered waterways. This is because covering a waterway alters the concentrations of its water quality parameters. This research is concerned with studying the
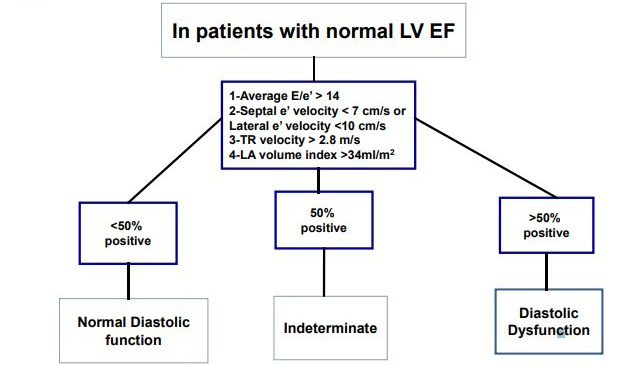
Left ventricular diastolic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with myocardial triglyceride content but not with impaired myocardial perfusion reserve
Purpose: To study myocardial perfusion reserve and myocellular metabolic alterations indicated by triglyceride content as possible causes of diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, preserved systolic function, and without clinically evident coronary artery disease. Materials and Methods: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (n = 42) underwent cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) for quantification of 1) myocardial contractility by strain-encoded MR (SENC); 2) myocardial triglyceride content by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy ( 1H-MRS); and 3) myocardial perfusion
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
