Breadcrumb
CoCoNUT: An efficient system for the comparison and analysis of genomes
Background: Comparative genomics is the analysis and comparison of genomes from different species. This area of research is driven by the large number of sequenced genomes and heavily relies on efficient algorithms and software to perform pairwise and multiple genome comparisons. Results: Most of the software tools available are tailored for one specific task. In contrast, we have developed a novel system CoCoNUT (Computational Comparative geNomics Utility Toolkit) that allows solving several different tasks in a unified framework: (1) finding regions of high similarity among multiple genomic
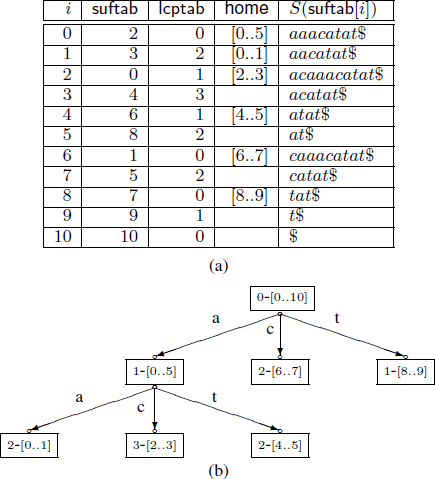
Fine tuning the enhanced suffix array
The enhanced suffix array is an indexing data structure used for a wide range of applications in Bioinformatics. It is basically the suffix array but enhanced with extra tables that provide extra information to improve the performance in theory and in practice. In this paper, we present a number of improvements to the enhanced suffix array: 1) We show how to find a pattern of length m in O(m) time, i.e., independent of the alphabet size. 2) We present an improved representation of the bucket table. 3) We improve the access time of addressing the LCP (longest common prefix) table when one byte
Finite element analysis of pulsatile blood flow in elastic artery
New hybrid Eulerian/Lagrangian model is presented accounting for the two-way coupling between the pulsating blood flow and the artery deformability. The Streamline-Upwind/Petrove--Galerkin (SUPG) finite element technique is used to treat for the convective nature of the momentum equation. The deformability of the artery walls is accounted for by treating the wall as an elastic beam under transverse unsteady distributed load, namely the fluid pressure. The results of the present contribution compare well against the available published data. © 2019, Isfahan University of Technology.
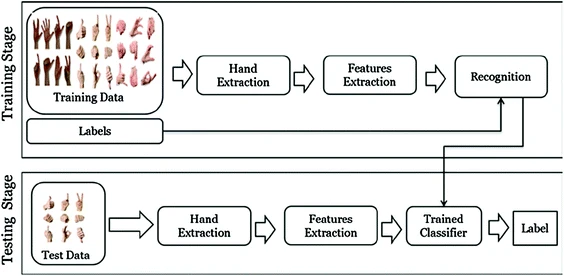
Gesture recognition for improved user experience in augmented biology lab
The Learning process in education systems is one of the most important issues that affect all societies. Advances in technology have influenced how people communicate and learn. Gaming Techniques (GT) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies provide new opportunities for a learning process. They transform the student’s role from passive to active in the learning process. It can provide a realistic, authentic, engaging and interesting learning environment. Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) is a major driver in the field of Augmented Reality (AR). In this paper, we propose an initiative Augmented
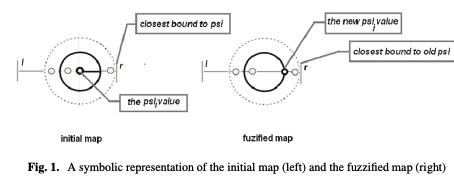
A fuzzy approach of sensitivity for multiple colonies on ant colony optimization
In order to solve combinatorial optimization problem are used mainly hybrid heuristics. Inspired from nature, both genetic and ant colony algorithms could be used in a hybrid model by using their benefits. The paper introduces a new model of Ant Colony Optimization using multiple colonies with different level of sensitivity to the ant’s pheromone. The colonies react different to the changing environment, based on their level of sensitivity and thus the exploration of the solution space is extended. Several discussion follows about the fuzziness degree of sensitivity and its influence on the
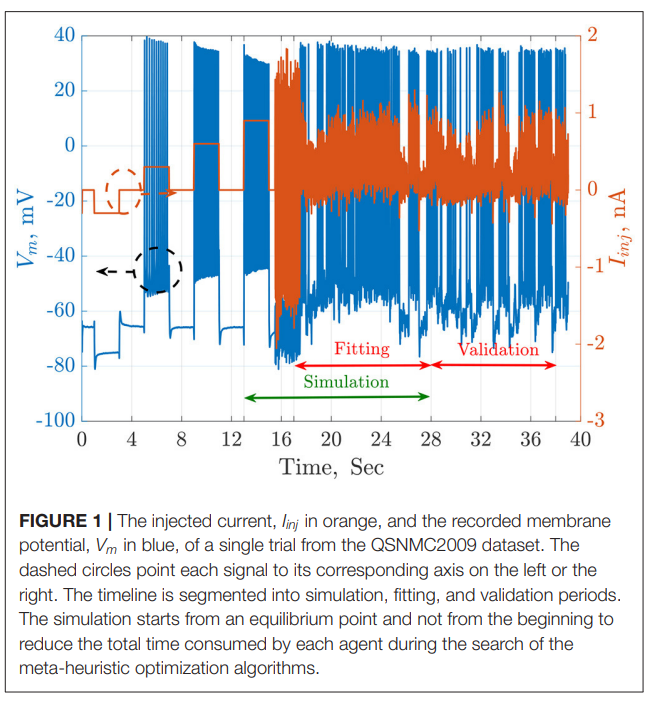
Parameter Estimation of Two Spiking Neuron Models With Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms
The automatic fitting of spiking neuron models to experimental data is a challenging problem. The integrate and fire model and Hodgkin–Huxley (HH) models represent the two complexity extremes of spiking neural models. Between these two extremes lies two and three differential-equation-based models. In this work, we investigate the problem of parameter estimation of two simple neuron models with a sharp reset in order to fit the spike timing of electro-physiological recordings based on two problem formulations. Five optimization algorithms are investigated; three of them have not been used to
Constructing suffix array during decompression
The suffix array is an indexing data structure used in a wide range of applications in Bioinformatics. Biological DNA sequences are available to download from public servers in the form of compressed files, where the popular lossless compression program gzip [1] is employed. The straightforward method to construct the suffix array for this data involves decompressing the sequence file, storing it on disk, and then calling a suffix array construction program to build the suffix array. This scenario, albeit feasible, requires disk access and throws away valuable information in the compressed
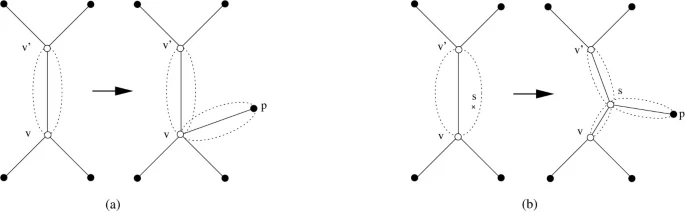
A fast algorithm for the multiple genome rearrangement problem with weighted reversals and transpositions
Background: Due to recent progress in genome sequencing, more and more data for phylogenetic reconstruction based on rearrangement distances between genomes become available. However, this phylogenetic reconstruction is a very challenging task. For the most simple distance measures (the breakpoint distance and the reversal distance), the problem is NP-hard even if one considers only three genomes. Results: In this paper, we present a new heuristic algorithm that directly constructs a phylogenetic tree w.r.t. the weighted reversal and transposition distance. Experimental results on previously
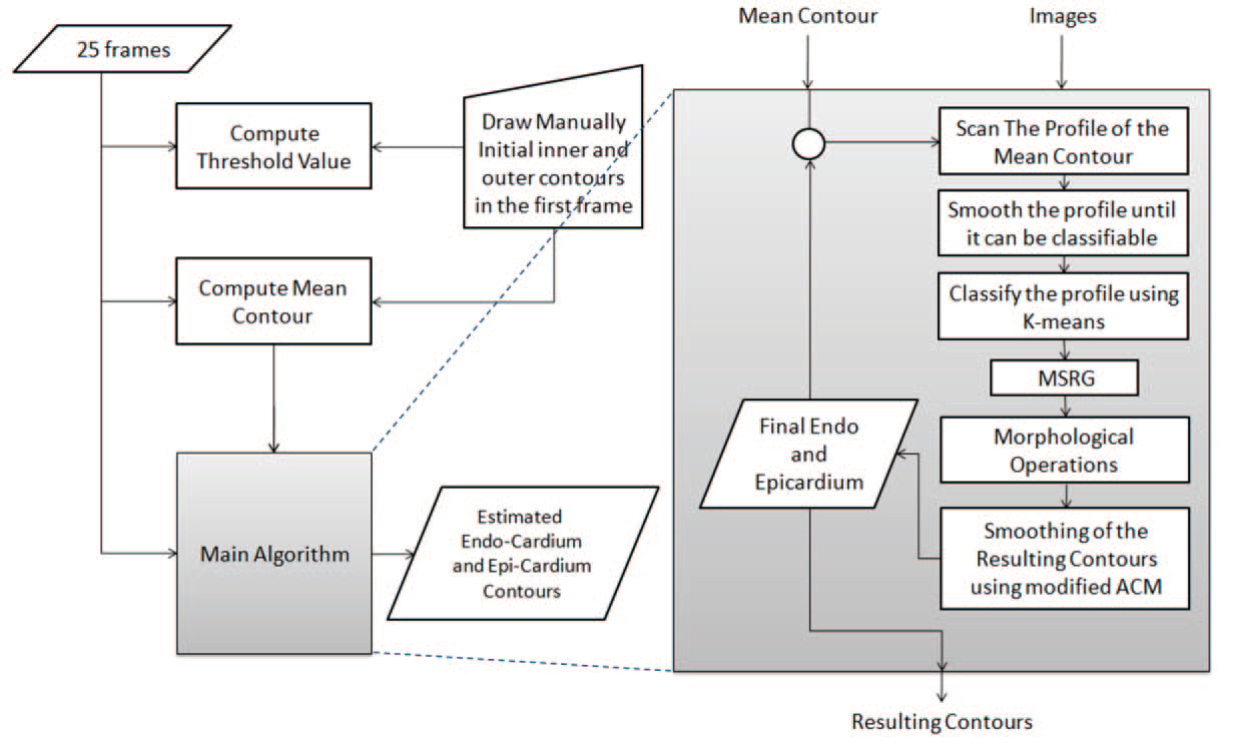
Segmentation of left ventricle in cardiac MRI images using adaptive multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
