Breadcrumb
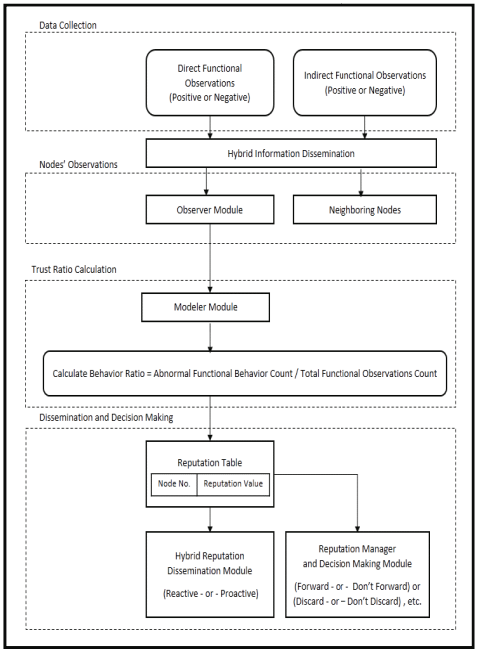
MDAC: A new reputation system for misbehavior detection and control in ad hoc networks
Reputation systems are an emerging area of research in ad-hoc networks. They have been introduced as a security solution for nodes' misbehaving problem. A reputation system should cope with any kind of misbehavior. It enables honest nodes to make fair decisions about their neighbors. This may encourage nodes to behave well and cooperate in order to avoid being penalized or isolated. In this paper, we propose a new reputation system for Misbehavior Detection And Control in ad hoc Networks (MDAC). It aims to overcome some of the unsolved issues of other reputation systems, and it is customizable
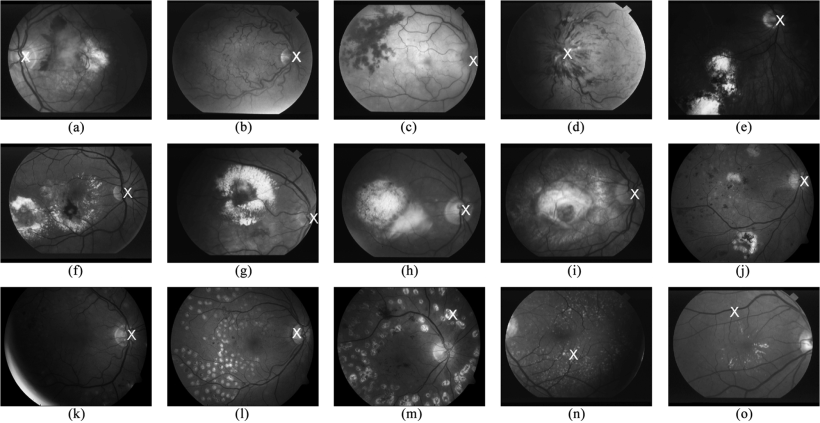
Fast localization of the optic disc using projection of image features
Optic Disc (OD) localization is an important pre-processing step that significantly simplifies subsequent segmentation of the OD and other retinal structures. Current OD localization techniques suffer from impractically-high computation times (few minutes per image). In this work, we present a fast technique that requires less than a second to localize the OD. The technique is based upon obtaining two projections of certain image features that encode the x- and y- coordinates of the OD. The resulting 1-D projections are then searched to determine the location of the OD. This avoids searching
Comparison study of digital forensics analysis techniques
Recently, digital forensics analysis got a great attention in IT security. This is especially after cyber incidents are getting new form of organized crime which introduced Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), and hacking Kill Chain definitions. The threat intense rises when it is affecting the healthcare organization where it will be life-threatening. Handling such incidents is a great challenge for handlers to uncover the attack steps. With various sources of evidential data that require analysis, one analysis technique can be more beneficial than another, comparing to the time and resources
Cluster Head election in Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) consist of a collection of cheap, easy to deploy Sensor nodes arranged together to fulfill a specific purpose (monitoring, tracking...etc.). A WSN network is composed of a Base Station (BS) and collection of sensors. There are a lot of approaches for the network construction. Amongst them is the hierarchical structure, where the network is divided into clusters and the node inside this cluster communicates with BS through a chosen leader called Cluster Head (CH). In this paper, we present cluster-Head election algorithms for WSNs. We will discuss the operations
CoCoNUT: An efficient system for the comparison and analysis of genomes
Background: Comparative genomics is the analysis and comparison of genomes from different species. This area of research is driven by the large number of sequenced genomes and heavily relies on efficient algorithms and software to perform pairwise and multiple genome comparisons. Results: Most of the software tools available are tailored for one specific task. In contrast, we have developed a novel system CoCoNUT (Computational Comparative geNomics Utility Toolkit) that allows solving several different tasks in a unified framework: (1) finding regions of high similarity among multiple genomic
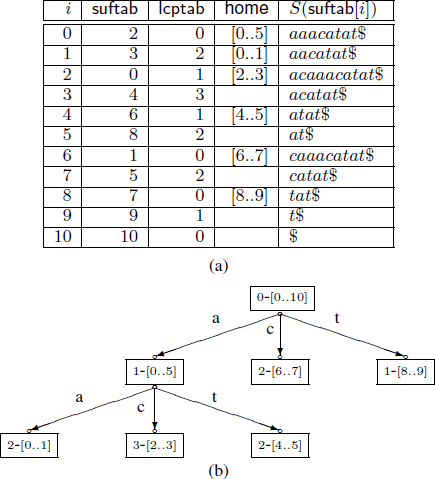
Fine tuning the enhanced suffix array
The enhanced suffix array is an indexing data structure used for a wide range of applications in Bioinformatics. It is basically the suffix array but enhanced with extra tables that provide extra information to improve the performance in theory and in practice. In this paper, we present a number of improvements to the enhanced suffix array: 1) We show how to find a pattern of length m in O(m) time, i.e., independent of the alphabet size. 2) We present an improved representation of the bucket table. 3) We improve the access time of addressing the LCP (longest common prefix) table when one byte
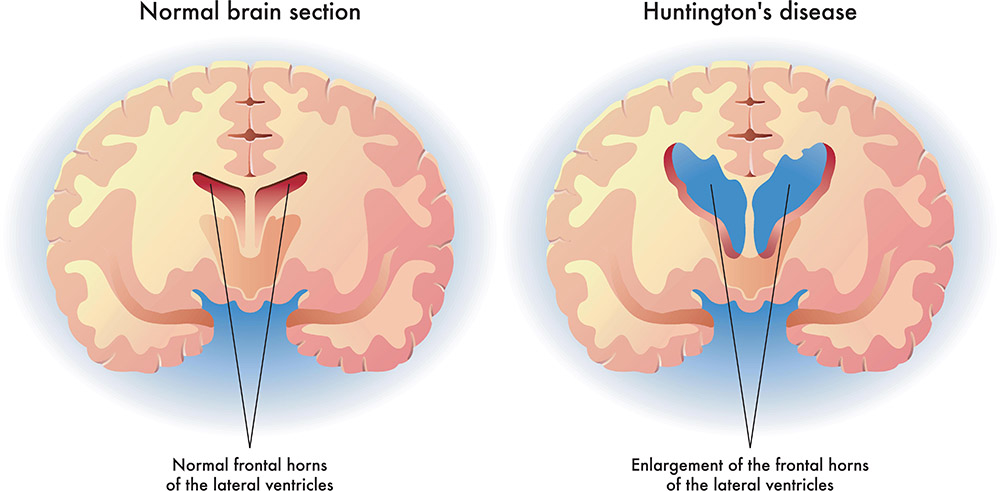
INVESTIGATION OF DIFFERENTIALLY EXPRESSED GENE RELATED TO HUNTINGTON'S DISEASE USING GENETIC ALGORITHM
neurodegenerative diseases have complex pathological mechanisms. Detecting disease-associated genes with typical differentially expressed gene selection approaches are ineffective. Recent studies have shown that wrappers Evolutionary optimization methods perform well in feature selection for high dimensional data, but they are computationally costly. This paper proposes a simple method based on a genetic algorithm engaged with the Empirical Bays T-statistics test to enhance the disease-associated gene selection process. The proposed method is applied to Affymetrix microarray data from
Towards mature temporal accuracy assessment of processors models and simulators for real-time systems development
Modeling and simulation are becoming extensively used in embedded and Real-Time Systems (RTSs) development throughout the development life-cycle, from the system-level design space exploration to the fine grained time analysis and evaluation of the system and even its components performance. At the core of these systems lies the processor which has been also the center of attention for most of the modeling and simulation efforts related to RTS simulation. Although the temporal accuracy of such models and simulators is of critical importance for Real-Time (RT) applications, it is not yet mature
Hardware Advancements Effects on MANET Development, Application and Research
Mobile devices' development has remarkably improved in light of the fast growing hardware advancements. These advancements include multicore processor chips, ultra large main memories and batteries that last for hours even when running modern applications such as file transfer, voice communication and video streaming ...etc. In this paper, we shed the light on recent and future trends of hardware advancements for mobile devices, and their impact on MANET developments. In addition, the effect of such advancements is investigated on application and different research areas. © Springer-Verlag
Reliability and Security Analysis of an Entanglement-Based QKD Protocol in a Dynamic Ground-to-UAV FSO Communications System
Quantum cryptography is a promising technology that achieves unconditional security, which is essential to a wide range of sensitive applications. In contrast to optical fiber, the free-space optical (FSO) link is efficiently used as a quantum channel without affecting the polarization of transmitted photons. However, the FSO link has several impairments, such as atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors, which affect the performance of the quantum channel. This paper proposes a quantum key distribution (QKD) scheme that uses a time-bin entanglement protocol over the FSO channel that suffers
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
