Breadcrumb
Guidance optimization for tactical homing missiles and air defense systems
The aim of this paper is to develop a functional approach to optimize the engagement effectiveness of the tactical homing missiles and air defense systems by utilizing the differential geometric concepts. In this paper the engagement geometry of the interceptor and the target is developed and expressed in differential geometric terms in order to demonstrate the possibilities of the impact triangles and specify the earliest interception based on the direct intercept geometry. Optimizing the missile heading angle and suitable missile velocity against the target velocity is then examined to
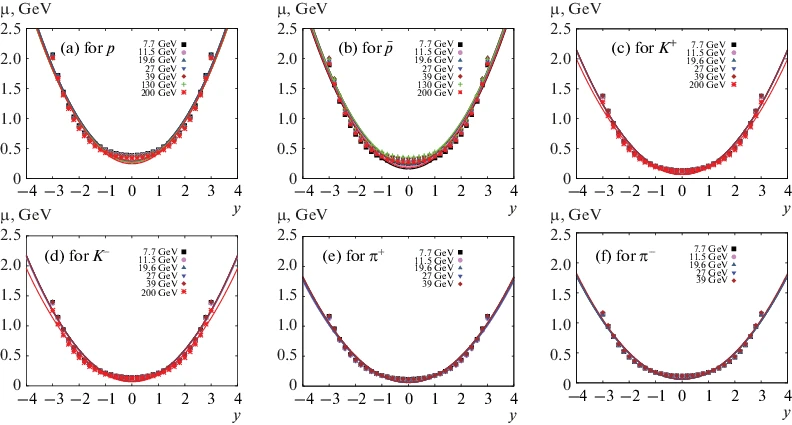
Almost Entirely Empirical Estimation for Chemical Potential
Abstract: Based on statistical thermal approaches, the transverse momentum distribution of the well-identified produced particles, π+, π–, K+, K–, p, and (Fromula presented.), is studied. We aim at introducing a novel almost entirely empirical estimation for the inclusive chemical potential μ. From the partition function of a grand-canonical ensemble, we propose a generic expression for the dependence of μ on the rapidity y. Then, by fitting this expression with the experimental results of the most central p⊥ and d2N/2πp⊥dp⊥dy, at 7.7, 11.5, 19.6, 27, 39, 130, 200 GeV, we introduce a generic
Hadronization correspondence of Hawking-Unruh radiation from rotating and electrically charged black holes
The proposed correspondence between the Hawking-Unruh radiation mechanism in rotating, electrically-charged, and electrically-charged-rotating black holes and the hadronization process in high-energy collisions is assumed here. This allows us to determine the well-profound freezeout parameters characterizing the heavy-ion collisions. Furthermore, black holes thermodynamics is found analogous to a to that of the high-energy collisions. We also introduce a relation expressing the dependence of the angular momentum and the angular velocity deduced from rotating black holes on the chemical

Determining the effect of changing channel geometry of irrigation canals on dissolved oxygen concentration
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important water quality parameter. It is considered the most important parameter. DO concentration in water is affected by different parameters such as volume flow rate, water velocity, and re-aeration rate. Those parameters are directly affected by the geometry of the waterway. Thus, studying the impact of changing channel geometry on DO is very important. Many researchers studied the effect of influential parameters on water quality variables but the influence of channel geometric parameters on DO was not studied thoroughly before. This research aims to study the

A critical review on green corrosion inhibitors based on plant extracts: Advances and potential presence in the market
Corrosion occurs in all sectors including oil pipelines, drinking water and sewerage in the majority of cases linked to corrosion of steel. Good corrosion management includes optimising corrosion control actions and minimising lifecycle corrosion costs whilst meeting environmental goals. The toxicity of commonly used synthetic inhibitors are the subject of recent legislations (REACH and PARCOM) have led to search on more eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Extensive research is conducted to assess the corrosion inhibition rate of diverse green inhibitors. However, it was not adequately
Multiplicity per rapidity in Carruthers and hadron resonance gas approaches
The multiplicity per rapidity of the well-identified particles π-, π+, k-, k+, p¯ , p, and p- p¯ measured in different high-energy experiments, at energies ranging from 6.3 to 5500 GeV, is successfully compared with the Cosmic Ray Monte Carlo event generator. For these rapidity distributions, we introduce a theoretical approach based on fluctuations and correlations (Carruthers approach) and another one based on statistical thermal assumptions (hadron resonance gas approach). Both approaches are fitted to both sets of results deduced from experiments and simulations. We found that the

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
Assessing leanness level with demand dynamics in a multi-stage production system
Purpose - The purpose of this paper is to present a dynamic model to measure the degree of system's leanness under dynamic demand conditions using a novel integrated metric. Design/methodology/approach - The multi-stage production system model is based on a system dynamics approach. The leanness level is measured using a new developed integrated metric that combines efficiency,WIP performance as well as service level. The analysis includes design of experiment technique at the initial analysis to examine the most significant parameters impacting the leanness score and then followed by
Towards Efficient Online Topic Detection through Automated Bursty Feature Detection from Arabic Twitter Streams
Detecting trending topics or events from Twitter is an active research area. The first step in detecting such topics focuses on efficiently capturing textual features that exhibit an unusual high rate of appearance during a specific timeframe. Previous work in this area has resulted in coining the term "detecting bursty features" to refer to this step. In this paper, TFIDF, entropy, and stream chunking are adapted to investigate a new technique for detecting bursty features from an Arabic Twitter stream. Experimental results comparing bursty features extracted from Twitter streams, to Twitter
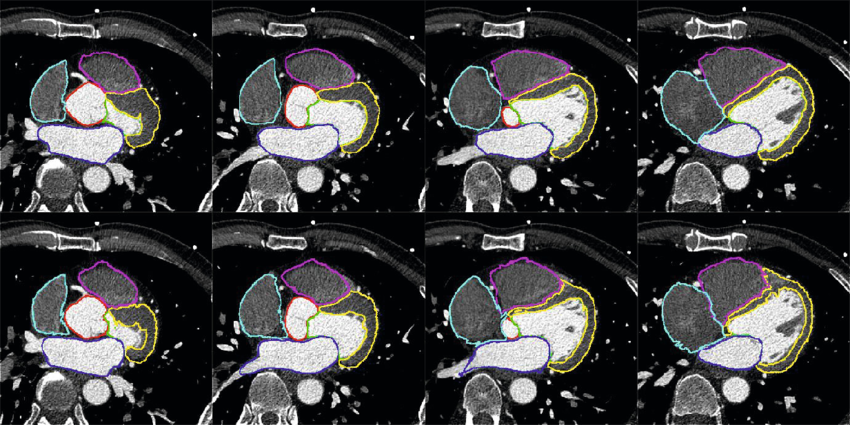
Myocardial segmentation using constrained multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
