Breadcrumb

A stochastic flight problem simulation to minimize cost of refuelling
Commercial airline companies are continuously seeking to implement strategies for minimizing costs of fuel for their flight routes as acquiring jet fuel represents a significant part of operating and managing expenses for airline activities. A nonlinear mixed binary mathematical programming model for the airline fuel task is presented to minimize the total cost of refueling in an entire flight route problem. The model is enhanced to include possible discounts in fuel prices, which are performed by adding dummy variables and some restrictive constraints, or by fitting a suitable distribution
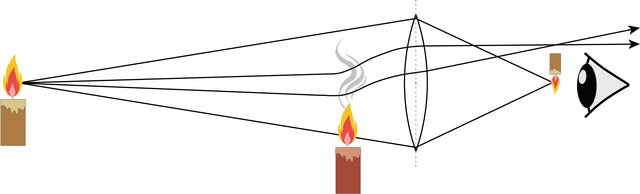
Design of a Schlieren System for Visualization of Heat and Mass Transfer
In this contribution, a simple yet effective design for Schlieren photography system is described and implemented. The proposed system is used in the visualization of both heat and mass transfer phenomena. Refractive index gradient is created by a lighter to study mass transfer, then the lighter is ignited to create temperature gradient. Results show the ability of the proposed system in capturing the gradients in both mass and temperature gradients. © 2020 IEEE.
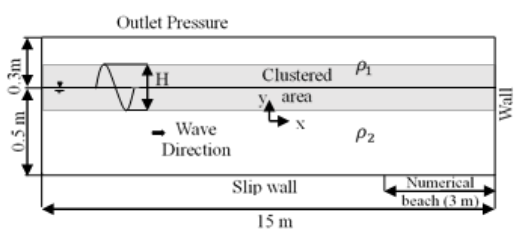
Simulation of Water Wave Interaction with Large Submerged Square Obstacles
Water waves propagation over submerged obstacles is considered. The problem serves as an efficient model for modeling breakwaters. A numerical wave tank is developed to simulate the induced flow field. The model is based on multiphase viscous flow assumptions. Computations are performed adopting clustered grids and suitable initial and boundary conditions. The results are verified using the flow field particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements. Spatial and temporal resolutions are validated. Complex flow phenomena occurring due to the presence of the relatively large sized obstacle are
Modified P3HT:PCBM Active Material with LiF Vertical Cylinders for Organic Solar Cells
In this paper, we introduce active material for an organic solar cell with a modified composition. A combination of P3HT: PCBM with parallel vertical LiF cylinders formulate the active material structure. The collection efficiency in the active material reaches 92.2%. The operating wavelength where the maximum collection efficiency occurs is adjusted and matched with the wavelength where the maximum irradiance of the solar spectrum occurs. The absorption per unit volume of the new structure is 80.4 μm-3 while the blank structure is 75.07 μm-3. The net absorption magnitude for the required
Analytical solution for fractional derivative gas-flow equation in porous media
In this paper, we introduce an analytical solution of the fractional derivative gas transport equation using the power-series technique. We present a new universal transform, namely, generalized Boltzmann change of variable which depends on the fractional order, time and space. This universal transform is employed to transfer the partial differential equation into an ordinary differential equation. Moreover, the convergence of the solution has been investigated and found that solutions are unconditionally converged. Results are introduced and discussed for the universal variable and other
Fractional-Order Model (FOM) for high-strength substrate biodegradation in conventional UASB reactor
This paper introduces a Fractional-Order Model (FOM) of Up-flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor for wastewater treatment regarding high-strength substrate biodegradation. The model can investigate the biogas production rate as well as the specific growth rate of bacteria with extra degree of freedom. Also, the hereditary effect of resident biomass on substrate degradation is studied on periodically long terms. Moreover, biomass concentration is examined in reactor under the influence of various fractional orders. Several numerical simulation results are introduced based on Grünwald
Modified kinetic-hydraulic UASB reactor model for treatment of wastewater containing biodegradable organic substrates
This paper addresses a modified kinetic-hydraulic model for up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor aimed to treat wastewater of biodegradable organic substrates as acetic acid based on Van der Meer model incorporated with biological granules inclusion. This dynamic model illustrates the biomass kinetic reaction rate for both direct and indirect growth of microorganisms coupled with the amount of biogas produced by methanogenic bacteria in bed and blanket zones of reactor. Moreover, the pH value required for substrate degradation at the peak specific growth rate of bacteria is
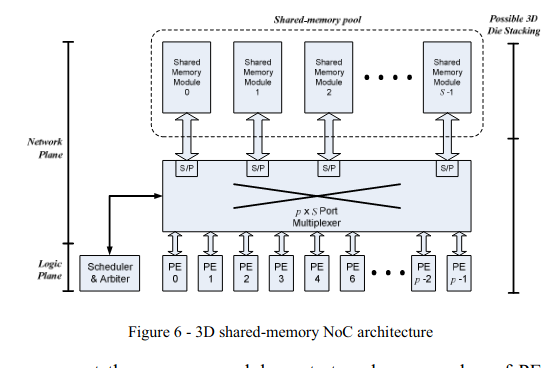
Novel 3D memory-centric NoC architecture for transaction-based SoC applications
Large and complex system-on-chip devices consisting of many processor cores, accelerators, DSP functions and many other processing and memory elements are becoming common in the semiconductor industry nowadays. To communicate, these processing and memory elements need to have a network-on-chip (NoC) that is scalable enough to support large number of elements and large bandwidth among other requirements. This paper evaluates the performance of the 2D memory-centric NoC architecture from throughput and latency perspective versus the Mesh topology. We also propose a memory-centric architecture
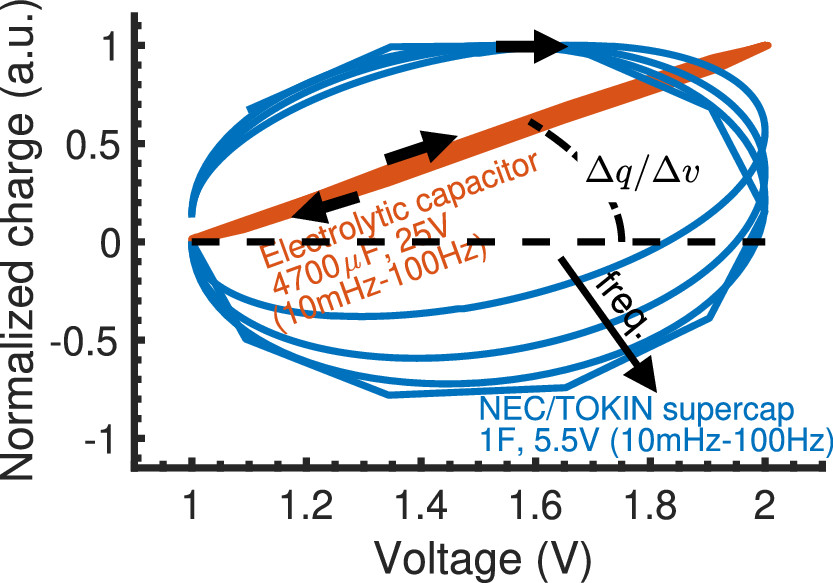
Frequency-dependent effective capacitance of supercapacitors using electrospun cobalt-carbon composite nanofibers
Mixing carbon-based materials with pseudocapacitive material is a widely used strategy to prepare high-energy, high-power supercapacitors. However, phase separation is inevitable after extended charging/discharging which leads to the degradation of performance metrics of the device. Here, we prepare in a single step cobalt-incorporated carbon nanofibers (CNF) by electrospinning homogeneous solutions of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) with cobalt acetate at different nominal proportions (1:0 to 1:1), and investigate their stability and capacitive behavior in symmetric supercapacitors. The
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››