Breadcrumb
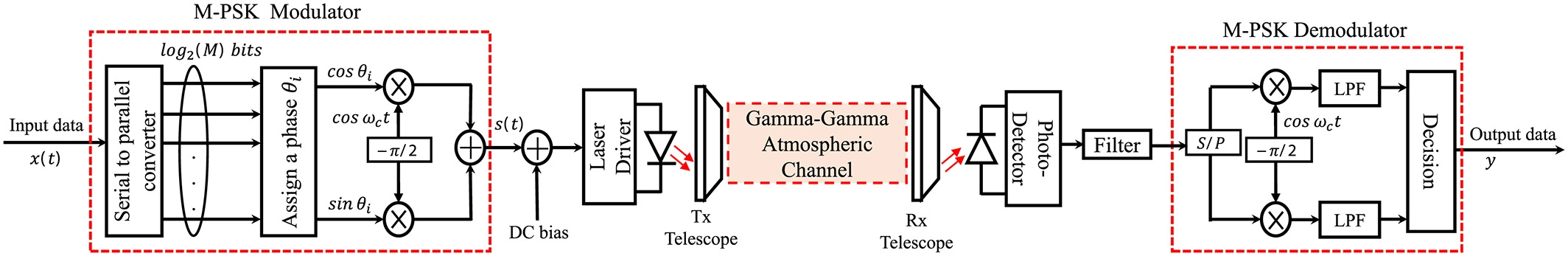
Enhancing spectral efficiency of FSO system using adaptive SIM/M-PSK and SIMO in the presence of atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors
This paper proposes an adaptive transmission modulation (ATM) technique for free-space optical (FSO) links over gamma-gamma turbulence channels.The ATM technique provides efficient utilization of the FSO channel capacity for improving spectral efficiency, by adapting the order of the phase-shift keying modulation scheme, according to the channel conditions and the required bit error rate (BER). To overcome the channel degradation resulting from the turbulence effects as well as the pointing errors (PEs), single-input multiple-output (SIMO) system with maximal ratio combining (MRC) is proposed
Digitizing material passport for sustainable construction projects using BIM
Several aspects hinder the application sustainability in construction industry. The most prominent problems are related to the conservation of natural resources and the generation of construction and demolition wastes. Previous studies indicated that these problems are due to lack of information available to construction projects stakeholders on the proper handling of building materials in their different lifecycle stages. This paper presents Material Passport (MP) tool that provides information on how to handle building materials at the construction stage and how to benefit from them at their
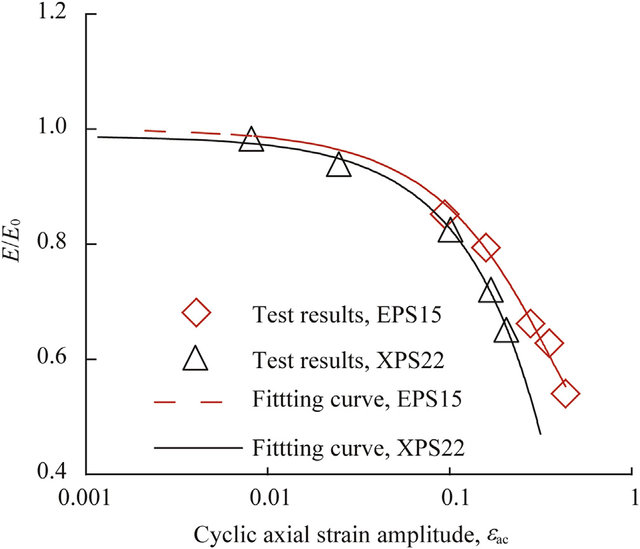
Ultrasonic characterization of expanded polystyrene used for shallow tunnels under seismic excitation
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is used as an inclusion to mitigate stresses acting on tunnels. In this study, the efficiency of utilizing EPS in reducing dynamic loads acting on shallow tunnels was studied. To gauge this, dynamic modulus of elasticity (Ed) and shear modulus (G) of EPS with densities equal to 25, 30, and 35 kg/m3 were characterized based on series of ultrasonic tests, where Ed ranged from 3500 to 6578 kPa, and G ranged from 1535 to 2741 kPa. A correlation was developed between EPS density and damping coefficient, which ranged from 1% to 2.3% based on G and the ultrasonic wave decay
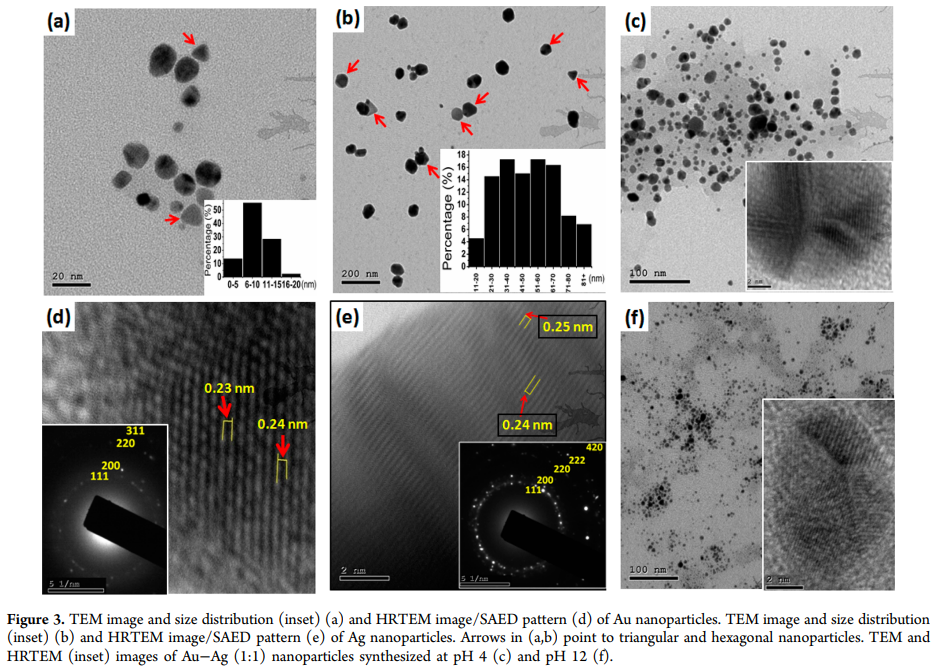
Phytosynthesis of Au, Ag, and Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles using aqueous extract of sago pondweed (Potamogeton pectinatus L.)
A green and facile method for the synthesis of Au, Ag, and Au-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles was developed using the aqueous extract of sago pondweed (Potamogeton pectinatus L.). Size, morphology, crystallinity, composition, capping layer, and stability of the synthesized nanoparticles were all investigated. The effect of the synthesis variables on the nanoparticles was also studied. Results showed that the synthesized nanoparticles were mostly spherical in shape, although other shapes as nanotriangles and hexagons were occasionally observed. Alloy-type Au-Ag nanoparticles could be synthesized at
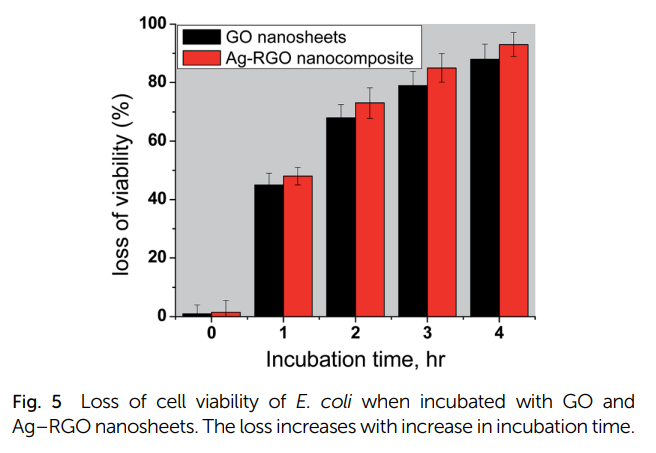
Phytosynthesis of silver-reduced graphene oxide (Ag-RGO) nanocomposite with an enhanced antibacterial effect using Potamogeton pectinatus extract
A new green synthesis method for the preparation of a silver-reduced graphene oxide (Ag-RGO) nanocomposite using Potamogeton pectinatus (Po) plant extract is introduced. The size, morphology and crystallinity of the as-prepared nanomaterials were studied with an explanation for the role of Po in the synthesis. A preliminary antibacterial experiment was developed to ensure the enhanced antibacterial effect of the Ag-RGO nanocomposite. The antibacterial measurements were done using the colony counting method. The results indicated that the majority of the silver nanoparticles "AgNPs" were formed
Discrete event simulation tool for earthmoving fleet selection
Earthmoving operations represent a sizable work in heavy civil engineering projects. Selecting optimum fleet configuration for an earthmoving operation is a very difficult process, especially when dealing with a multi loader type and multi truck type configurations. This paper presents a framework that can be used for the selection of optimum fleet for earthmoving operations. It enables the user to input the available loading and hauling equipment, then, it calculates the cost and total project time of each possible fleet combination, and finally it provides a list of the top-ten best fleet
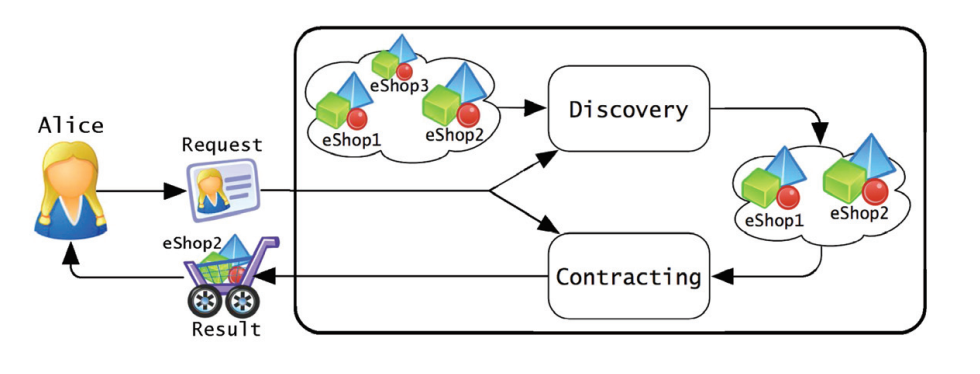
Knowledge management in contract administration: An ontological engineering approach
Knowledge has been identified to be a significant organizational resource, which if used effectively can provide competitive advantage. Construction contract administration is a complex, knowledge-intensive process that if properly managed can mitigate the contractor's risk exposure. Challenges in proper knowledge management of contract administration are due to: 1) Large amount of fragmented information that is required to manage a construction contract, 2) Information located in heterogeneous sources (Request For Information (RFIs), site notices, schedules, contracts, etc...), 3) Information
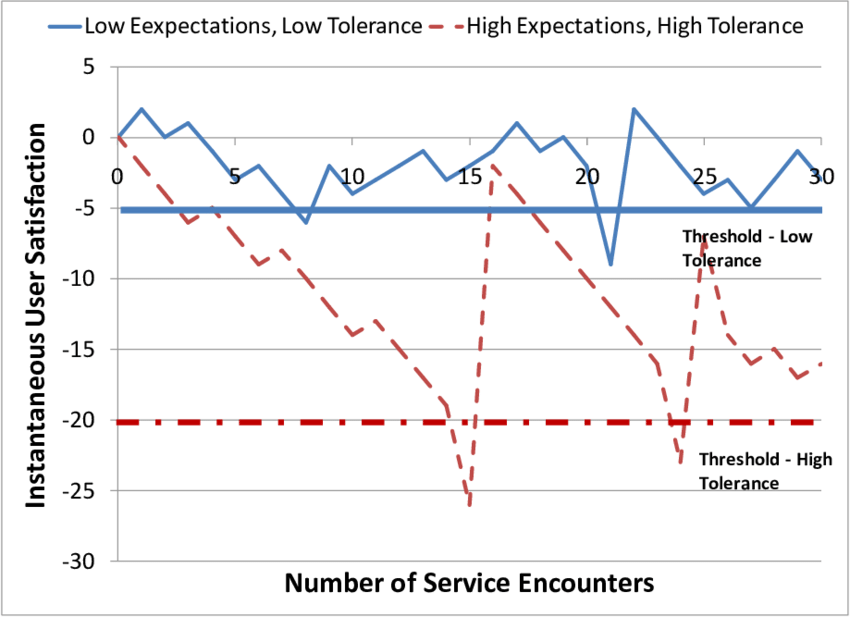
Modeling user behavior and infrastructure level of service: An agent-based simulation approach
Traditional modeling frameworks used for infrastructure asset management have suffered from two main shortcomings. Most approaches have focused their modeling efforts on the infrastructure asset itself, thereby ignoring the multitude of interactions that occur between other entities. In addition, an a-priori behavior of all elements in the modeling environment has always been assumed. This paper argues that these shortcomings have significantly limited the decision-making capabilities of infrastructure asset management systems by limiting their ability to simulate emergent behavior that is
Predicting telecommunication tower costs using fuzzy subtractive clustering
This paper presents a fuzzy subtractive modelling technique to predict the weight of telecommunication towers which is used to estimate their respective costs. This is implemented through the utilization of data from previously installed telecommunication towers considering four input parameters: a) tower height; b) allowed tilt or deflection; c) antenna subjected area loading; and d) wind load. Telecommunication towers are classified according to designated code (TIA-222-F and TIA-222-G standards) and structures type (Self-Supporting Tower (SST) and Roof Top (RT)). As such, four fuzzy
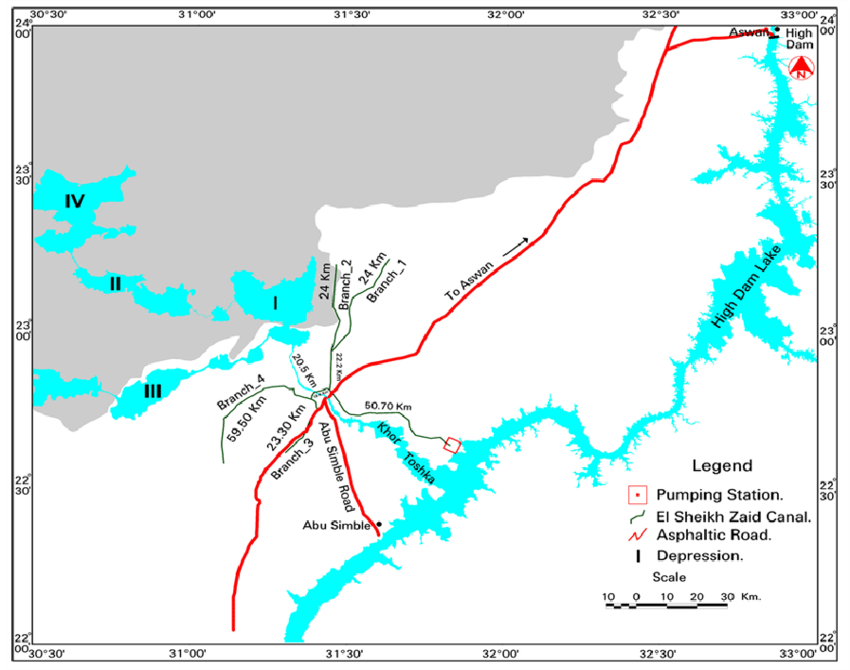
Effect of solar canals on evaporation, water quality, and power production: An optimization study
Both energy and availability of water with good quality are essential for the well-being of humans. Thus, it is very important to study the parameters that would affect water quality, so as to come up with mitigation measures if water quality would be at risk or negatively affected. Moreover, it is very important to always search for new energy resources, especially if they are renewable. This research study is concerned with studying solar canals and their effect on evaporation and water quality variables of canals covered by solar cells, as well as the effect on power production. Both a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 5
- Next page ››
