Breadcrumb
Ergonomic analysis of a working posture in steel industry in Egypt using digital human modeling
This study presents solutions for improving a bending awkward posture in steel industry in Egypt using digital Human Modeling (DHM). The information is gathered by interviewing the workers, working postures are recorded via a video camera while the worker is performing his usual work. The postures are analyzed using DHM software. Porter comfort analysis and Rapid Upper Limb Assessment are applied for postures analysis. The analysis shows high levels of discomfort in neck, trunk, leg and forearm. These discomforts could cause permanent injuries over long periods. A modified design is proposed
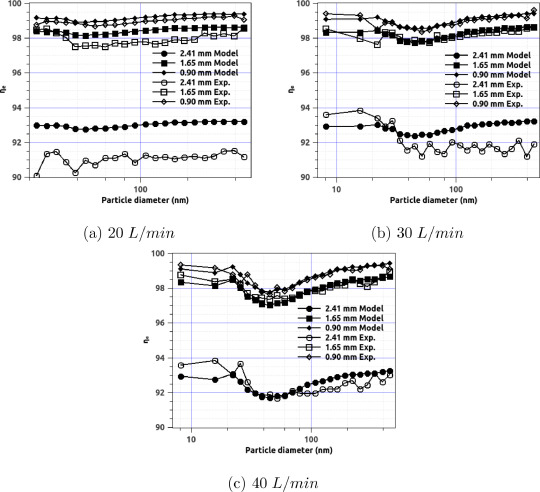
An analytical model for the effective filtration efficiency of single and multiple face masks considering leakage
An analytical model for the filtration efficiency of face masks is developed. The model considers the effect of gap leakage due to the improper fitting of the face mask in the reduction of the effective filtration efficiency. The model is also extended to include the case with multiple face masks. The model results are verified using experimental data from literature. It is shown that the adverse effect of the gap leakage depends on the face mask filtration and leakage characteristics. It is also shown that wearing more than one face mask might not always be beneficial in some scenarios
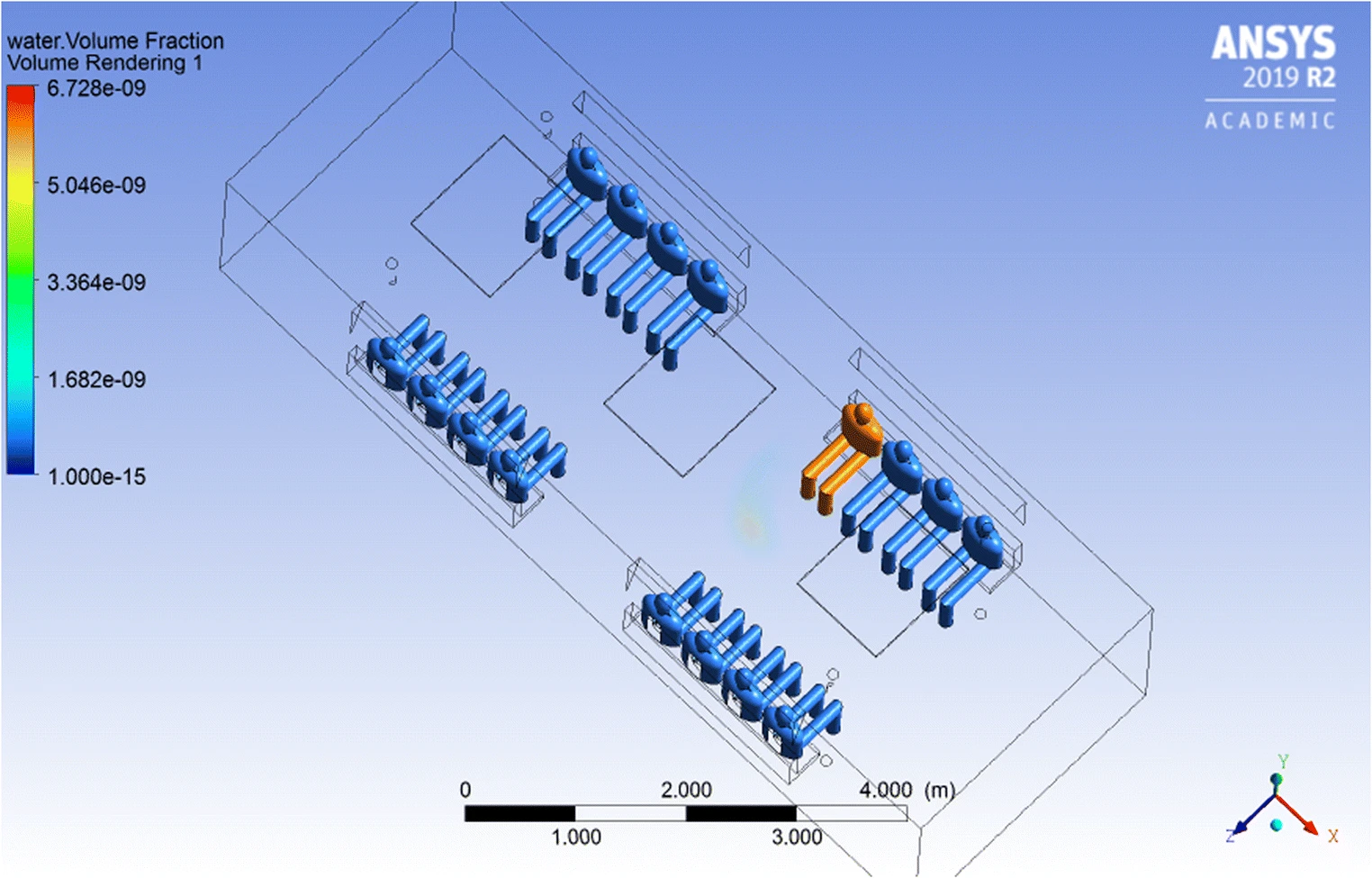
Air change rate effects on the airborne diseases spreading in Underground Metro wagons
The effect of the rate of change of fresh air inside passengers’ wagons for Underground Metro on the spreading of airborne diseases like COVID-19 is investigated numerically. The study investigates two extreme scenarios for the location of the source of infection within the wagon with four different air change rates for each. The first scenario considers the source of infection at the closest point to the ventilation system while the other places the infection source at the farthest point from the wagon ventilation system. The effect of the wagon windows’ status (i.e. closed or open) is also
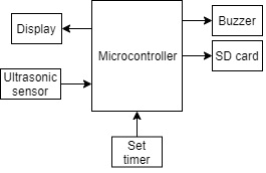
Simulation of vitiligo therapy equipment
Vitiligo is a skin disorder caused by a lack of melanin pigment in the skin, which causes white patches on certain parts of the skin because this melanin pigment is not able to produce the skin color. Previously, one of the treatments for vitiligo was using a UVB lamp with a 311 nm wavelength that could not yet be adjusted to dim the lights as safety when conducting therapy. Therefore, the research aims to design a simulation of the vitiligo therapy device equipped with a timer LED lamp, a safety of lighting, and the data storage. The data are stored in the SD Card to make it easier for
Medical nanorobots: Design, applications and future challenges
Following the current technological revolution, the concept of emerging fields and getting a common benefit becomes a bright way to follow. Going deeper in nanotechnology, nanorobotics has been the glimpse of hope in many fields; particularly, in the medical field. Nanorobotics applications in medicine are divided into two main categories, diagnosis and treatment, and extensive efforts have been given to research about its operation principles and design. Unfortunately, problem have emerged regarding the implementation, methods of actuation, and customized components of nanorobotics to be used
Optimum Location of Field Hospitals for COVID-19: A Nonlinear Binary Metaheuristic Algorithm
Determining the optimum location of facilities is critical in many fields, particularly in healthcare. This study proposes the application of a suitable location model for field hospitals during the novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The used model is the most appropriate among the threemost common locationmodels utilized to solve healthcare problems (the set covering model, the maximal covering model, and the P-median model). The proposed nonlinear binary constrained model is a slight modification of the maximal covering model with a set of nonlinear constraints. The model is used to
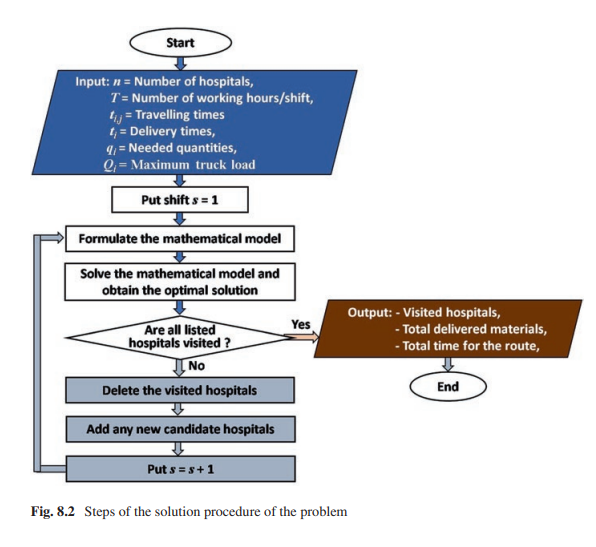
Optimum distribution of protective materials for COVID−19 with a discrete binary gaining-sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm
Many application problems are formulated as nonlinear binary programming models which are hard to be solved using exact algorithms especially in large dimensions. One of these practical applications is to optimally distribute protective materials for the newly emerged COVID-19. It is defined for a decision-maker who wants to choose a subset of candidate hospitals comprising the maximization of the distributed quantities of protective materials to a set of chosen hospitals within a specific time shift. A nonlinear binary mathematical programming model for the problem is introduced with a real
Comparative Analysis of Various Machine Learning Techniques for Epileptic Seizures Detection and Prediction Using EEG Data
Epileptic seizures occur as a result of functional brain dysfunction and can affect the health of the patient. Prediction of epileptic seizures before the onset is beneficial for the prevention of seizures through medication. Electroencephalograms (EEG) signals are used to predict epileptic seizures using machine learning techniques and feature extractions. Nevertheless, the pre-processing of EEG signals for noise removal and extraction of features are two significant problems that have an adverse effect on both anticipation time and true positive prediction performance. Considering this, the
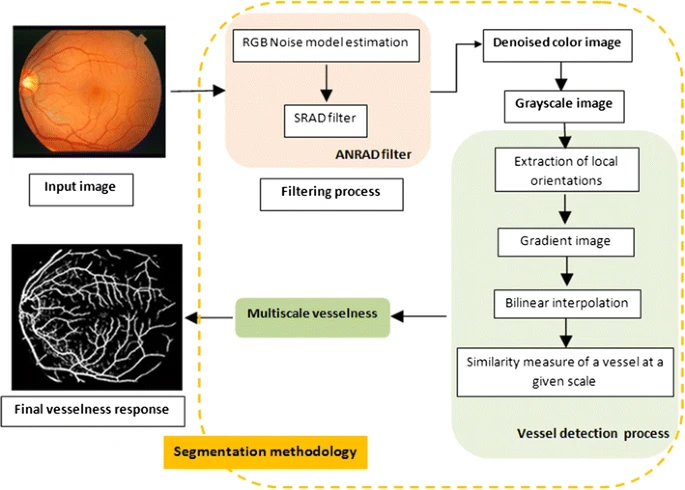
Noise-estimation-based anisotropic diffusion approach for retinal blood vessel segmentation
Recently, numerous research works in retinal-structure analysis have been performed to analyze retinal images for diagnosing and preventing ocular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, which is the first most common causes of vision loss in the world. In this paper, an algorithm for vessel detection in fundus images is employed. First, a denoising process using the noise-estimation-based anisotropic diffusion technique is applied to restore connected vessel lines in a retinal image and eliminate noisy lines. Next, a multi-scale line-tracking algorithm is implemented to detect all the blood
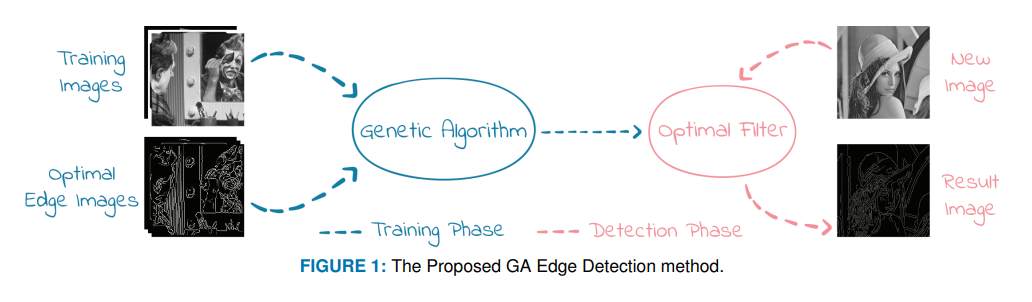
Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumor Detection in MR Images
Genetic algorithms (GAs) are intended to look for the optimum solution by eliminating the gene strings with the worst fitness. Hence, this paper proposes an optimized edge detection technique based on a genetic algorithm. A training dataset that consists of simple images and their corresponding optimal edge features is employed to obtain the optimum filter coefficients along with the optimum thresholding algorithm. Qualitative and quantitative performance analyses are investigated based on several well-known metrics. The performance of the proposed genetic algorithm-based cost minimization
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
