Breadcrumb
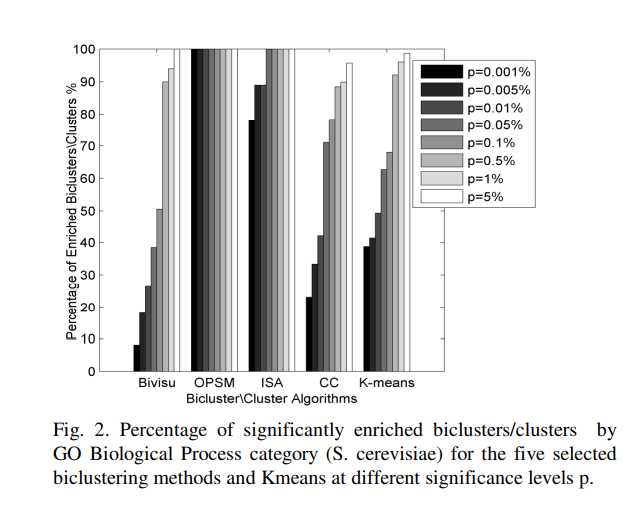
An automatic gene ontology software tool for bicluster and cluster comparisons
We propose an Automatic Gene Ontology (AGO) software as a flexible, open-source Matlab software tool that allows the user to easily compare the results of the bicluster and cluster methods. This software provides several methods to differentiate and compare the results of candidate algorithms. The results reveal that bicluster/cluster algorithms could be considered as integrated modules to recover the interesting patterns in the microarray datasets. The further application of AGO could to solve the dimensionality reduction of the gene regulatory networks. Availability: AGO and help file is
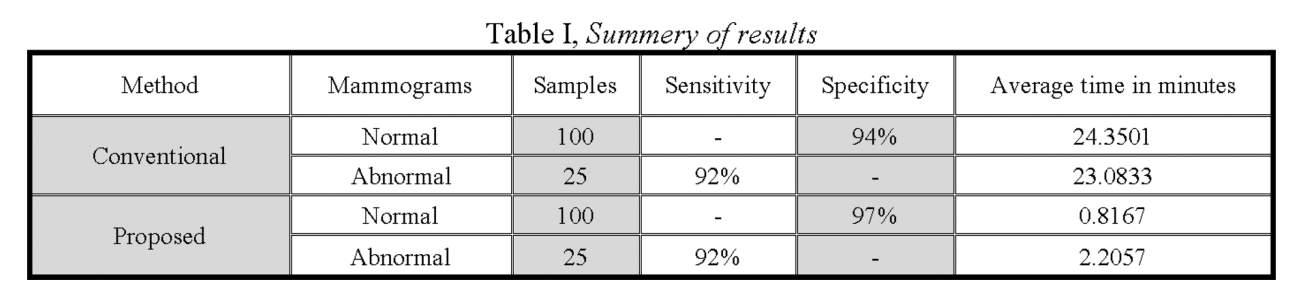
Fast fractal modeling of mammograms for microcalcifications detection
Clusters of microcalcifications in mammograms are an important early sign of breast cancer in women. Comparing with microcalcifications, the breast background tissues have high local self-similarity, which is the basic property of fractal objects. A fast fractal modeling method of mammograms for detecting the presence of microcalcifications is proposed in this paper. The conventional fractal modeling method consumes too much computation time. In the proposed method, the image is divided into shade (homogeneous) and non-shade blocks based on the dynamic range and only the non-shade blocks are
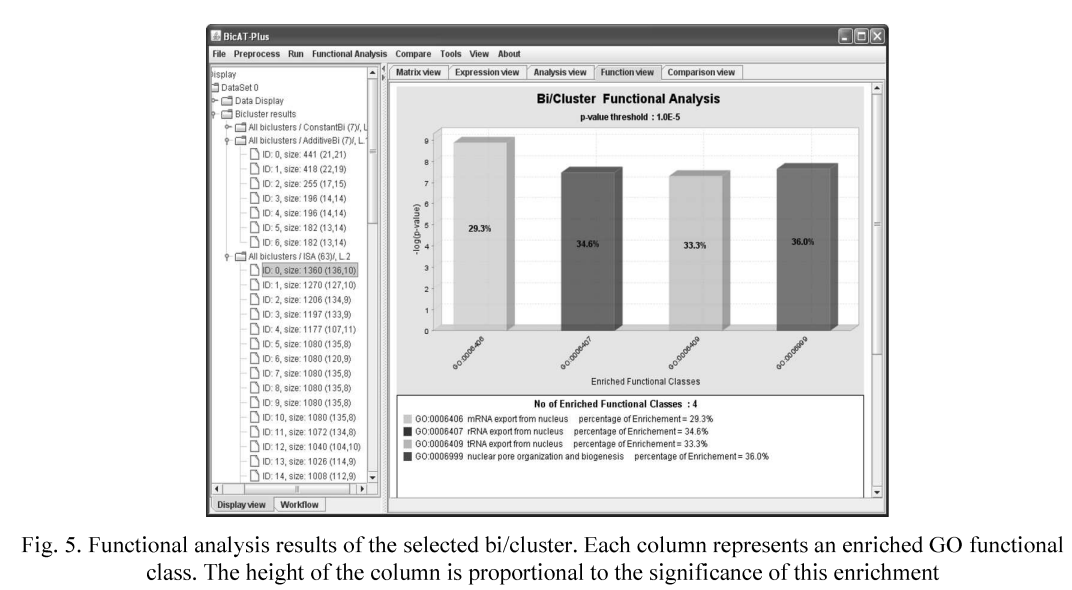
BicATPlus: An automatic comparative tool for Bi/Clustering of gene expression data obtained using microarrays
In the last few years the gene expression microarray technology has become a central tool in the field of functional genomics in which the expression levels of thousands of genes in a biological sample are determined in a single experiment. Several clustering and biclustering methods have been introduced to analyze the gene expression data by identifying the similar patterns and grouping genes into subsets that share biological significance. However, it is not clear how the different methods compare with each other with respect to the biological relevance of the biclusters and clusters as well
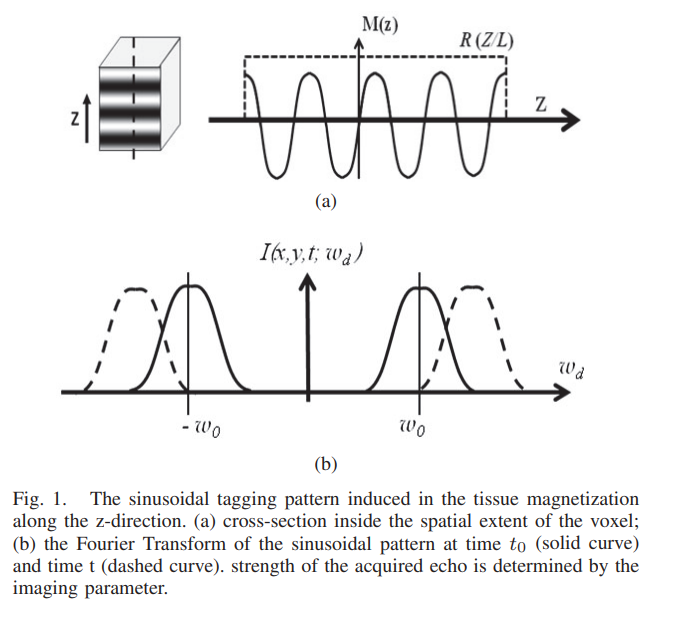
Maximum likelihood estimator for signal intensity in STEAM-based MR imaging techniques
Stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) is a generic imaging technique that lies at the core of many magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques such MRI tagging, displacement encoded MRI, black-blood cardiac imaging. Nevertheless, tissue deformation causes frequency shift of the MR signal and leads to severe signal attenuation. In this work, a maximum likelihood estimator for the signal amplitude is proposed and used to correct the image artifacts. Numerical simulation and real MR data are used to test and validate the proposed method. © 2011 IEEE.

Ambient and wearable sensing for gait classification in pervasive healthcare environments
Pervasive healthcare environments provide an effective solution for monitoring the wellbeing of the elderly where the general trend of an increasingly ageing population has placed significant burdens on current healthcare systems. An important pervasive healthcare system functionality is patient motion analysis where gait information can be used to detect walking behavior abnormalities that may indicate the onset of adverse health problems, for quantifying post-operative recovery, and to observe the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of accurate motion analysis models
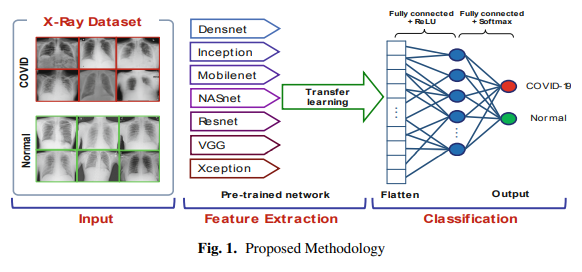
Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-Ray Images Using Deep Neural Network with Fine-Tuning Approach
The coronavirus (COVID-2019) quickly spread throughout the world and came to be a pandemic. To avoid further spreading this epidemic and treat affected patients rapidly, it is important to recognize the positive cases as early as possible. In this paper, deep learning techniques are employed to detect COVID-19 from chest X-ray images quickly. The images of the two classes, COVID and No-findings are collected from three public datasets. The proposed approach consists of two phases; transfer learning and fine-tuning. Transfer learning is carried out by seven deep learning models: DenseNet
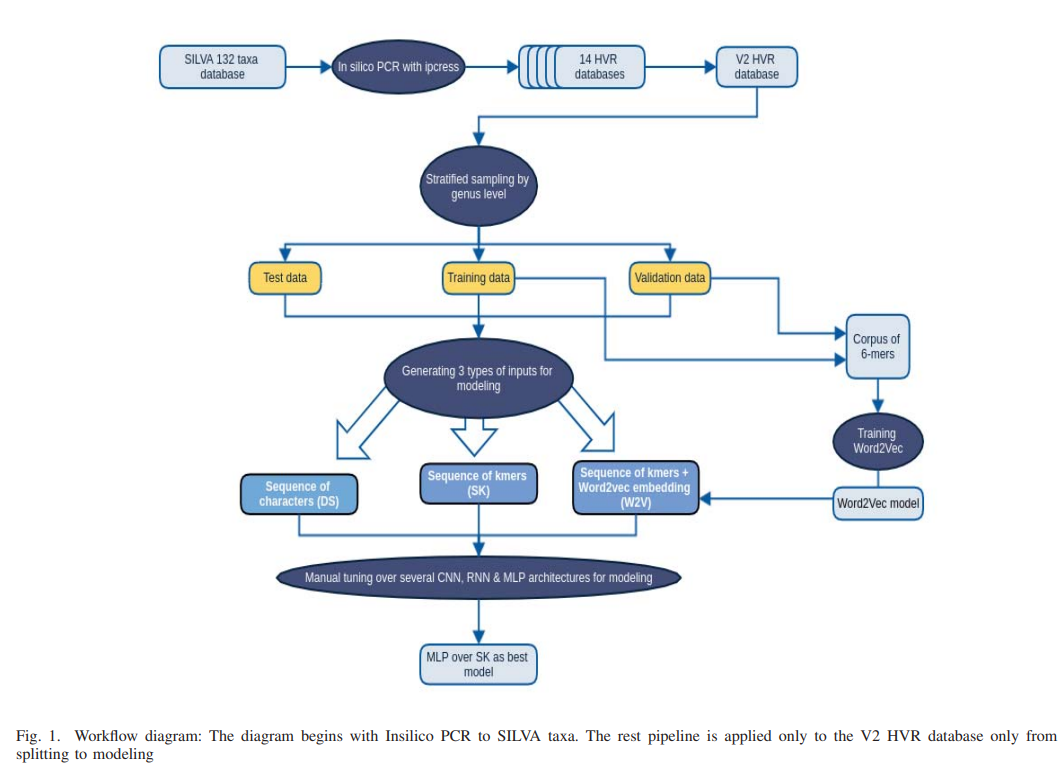
AmpliconNet: Sequence Based Multi-layer Perceptron for Amplicon Read Classification Using Real-time Data Augmentation
Taxonomic assignment is the core of targeted metagenomics approaches that aims to assign sequencing reads to their corresponding taxonomy. Sequence similarity searching and machine learning (ML) are two commonly used approaches for taxonomic assignment based on the 16S rRNA. Similarity based approaches require high computation resources, while ML approaches dont need these resources in prediction. The majority of these ML approaches depend on k-mer frequency rather than direct sequence, which leads to low accuracy on short reads as k-mer frequency doesnt consider k-mer position. Moreover
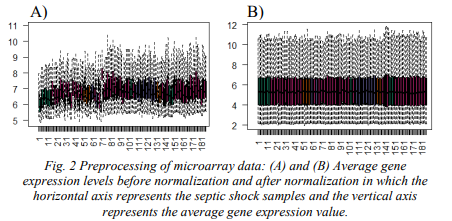
Studying Genes Related to the Survival Rate of Pediatric Septic Shock
Pediatric septic shock is generally considered as a devastating clinical syndrome that can lead to tissue damage and organ failure due to the over exaggerated immune response to an infection. Therefore, in this paper, we attempted to early identify the clinical course of such disease with the aid of peripheral blood T-cells of 181 pediatric patients who admitted to Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Accordingly, 34 differential expressed genes have been identified as biological genetic biomarkers. Minimum redundancy and maximum relevance feature selection strategy has been proposed for the discovery
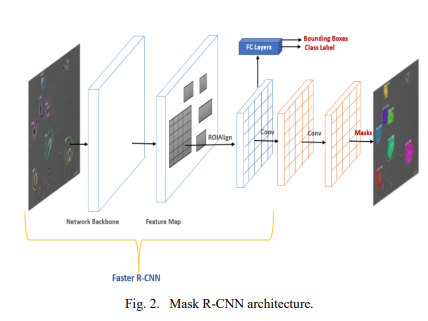
Instance Segmentation of 2D Label-Free Microscopic Images using Deep Learning
The precise detection and segmentation of cells in microscopic image sequences is an essential task in biomedical research, such as drug discovery and studying the development of tissues, organs, or entire organisms. However, the detection and segmentation of cells in phase contrast images with a halo and shade-off effects is still challenging. Lately, Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN) has been introduced for object detection and instance segmentation of natural images. This study investigates the efficacy of the Mask R-CNN to instantly detect and segment label-free
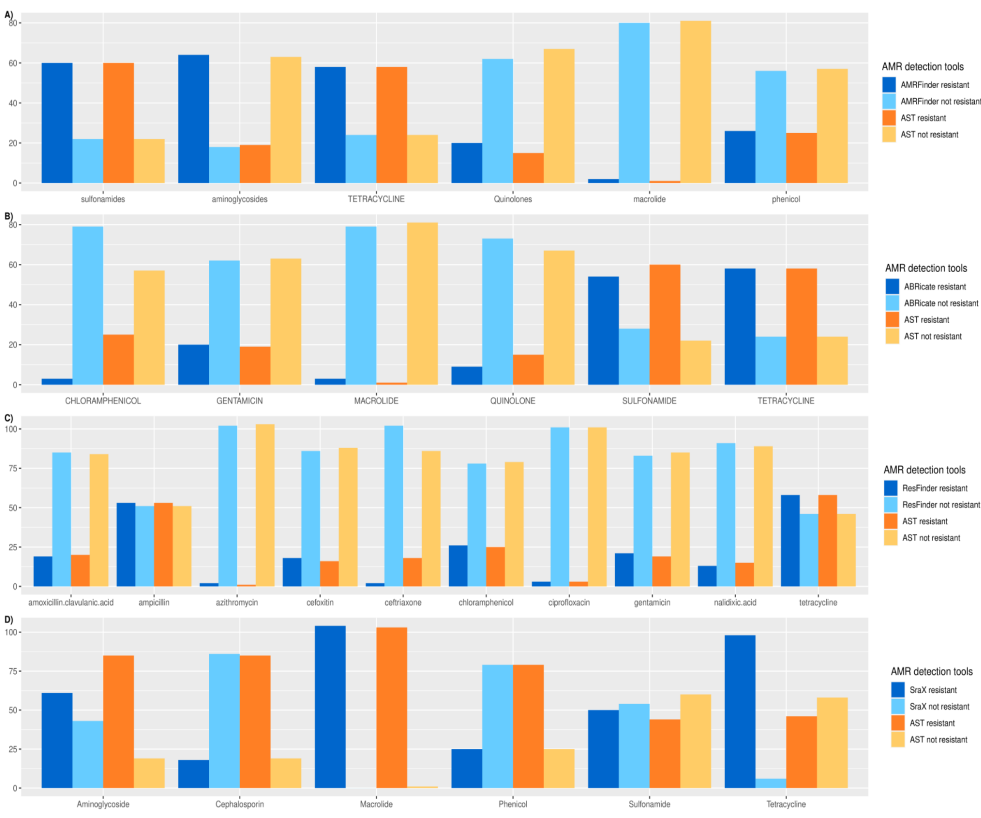
Benchmarking of Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Detection Tools in Assembled Bacterial Whole Genomes
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the ten dangers threatening our world, according to the world health organization (WHO). Nowadays, there are plenty of electronic microbial genomics and metagenomics data records that represent host-associated microbiomes. These data introduce new insights and a comprehensive understanding of the current antibiotic resistance threats and the upcoming resistance outbreak. Many bioinformatics tools have been developed to detect the AMR genes based on different annotated databases of bacterial whole genome sequences (WGS). The number and structure of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
