Breadcrumb

Modeling and control of 3-omni wheel Robot using PSO optimization and Neural Network
Omni mobile robots are one of the mobile robots that interact with humans in many areas where it is needed to be collaborative and accurate. Committing robotics with artificial intelligence-based controllers became nowadays mandatory for more association of these robots with distinct environments. This paper proposes the distinction of the 3WD Omni Vision feedback model between Simscape and actual information to obtain a surmised model. Study applying some artificial control procedures on this model for path planning and speed control as the artificial neural system and PSO optimization

Active Morphing Control of Airfoil At Low Reynolds Number Using Level-Set Method
The active control of flow around an airfoil through morphing is numerically investigated. The lock-in phenomenon was predicted while using a fixed grid. Galerkin/Least-Squares Finite Element Method was used to simulate incompressible flow over an airfoil with leading edge morphing at a Reynolds number, Re = 5000, and angle of attack, α = 6°. The numerical simulation was carried out using the in-house FORTRAN code. The code was validated with the literature by simulating the flow over an oscillating cylinder. The paperwork implemented a locally oscillating surface on the airfoil with a
Self-Driving Car Lane-keeping Assist using PID and Pure Pursuit Control
Detection of lane boundaries is the primary role for monitoring an autonomous car's trajectory. Three lane identification methodologies are explored in this paper with experimental illustration: Edge detection, Hough transformation, and Birds eye view. The next step after obtaining the boundary points is to add a regulation rule to effectively trigger the regulation of steering and velocity to the motors. A comparative analysis is made between different steering controllers like PID or by using PID with a pure pursuit controller for the Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) system. A camera that sends

A Neuro-Fuzzy Based Approach for Energy Consumption and Profit Operation Forecasting
In recent years, the massive growth in the scale of data is being a key factor in the needed data processing approaches. The efficiency of the algorithms of knowledge extraction depends significantly on the quality of the raw data, which can be improved by employing preprocessing techniques. In the field of energy consumption, the forecasting of power cost needed plays a vital role in determining the expected profit. To achieve a forecasting with higher accuracy, it is needed to deal with the large amount of data associated with power plants. It is shown in the literature that the use of
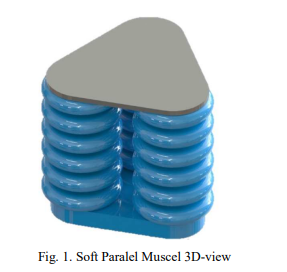
Design and FEA-based Methodology for a Novel 3 Parallel Soft Muscle Actuator
Recently, soft robotics represents a new era of advanced robotics systems. Based on the flexible nature of soft robots, they are more adequate to have safe interaction with humans and handle complex or delicate objects. Due to the nature of soft robotics, there is a crucial need to propose new designs, fabrication, and control systems suitable for the flexibility nature. In this research project, a novel three parallel soft muscle actuator is proposed. The proposed design and analytical models for predicting actuation behavior are based on a set of design parameters. First, the actuator

Metaheuristic Optimization of Fractional Order Incremental Conductance (FO-INC) Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
This paper seeks to improve the photovoltaic (PV) system efficiency using metaheuristic, optimized fractional order incremental conductance (FO-INC) control. The proposed FO-INC controls the output voltage of the PV arrays to obtain maximum power point tracking (MPPT). Due to its simplicity and efficiency, the incremental conductance MPPT (INC-MPPT) is one of the most popular algorithms used in the PV scheme. However, owing to the nonlinearity and fractional order (FO) nature of both PV and DC-DC converters, the conventional INC algorithm provides a trade-off between monitoring velocity and
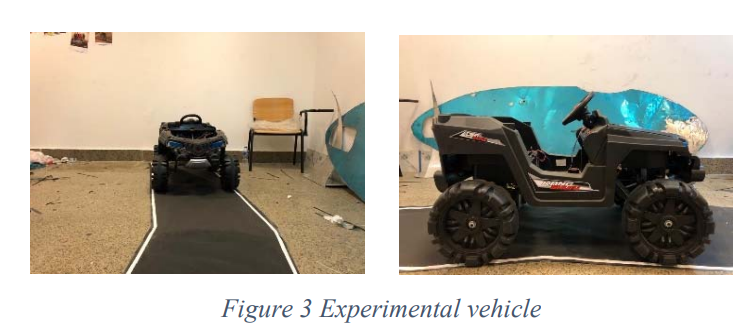
Steering Control for Autonomous Vehicles Using PID Control with Gradient Descent Tuning and Behavioral Cloning
In this paper we implement and evaluate two ways of controlling the steering angle of an autonomous vehicle, PID control with manual tuning followed by gradient descent algorithm tuning-which is able to enhance the performance through self-adjusting the controller parameters-and using supervised machine learning through the end-to-end deep learning for self-driving car which implement Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to predict the steering angle for a given instance of a track. The verification testing went through two phases: software simulation using python for first run testing and C++

Lid-Driven Cavity Flow with Elliptic Obstacle at Different Orientations
The aim of the present work is to predict the flow field around an elliptic obstacle at different orientations inside a square Lid-Driven Cavity (LDC). The Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) is used to simulate the flow at a Reynolds number, Re, of 100, using the two-dimensional nine-velocity, (D2Q9) lattice configuration and the BGK collision operator. The in-house code is validated using data from the literature for the case of LDC with a central circular cylinder. Different ellipse orientations are tested (0°, 30°, 45°, 90°, 120°, 145°, and 150°) to check the effect of orientation on the vortex
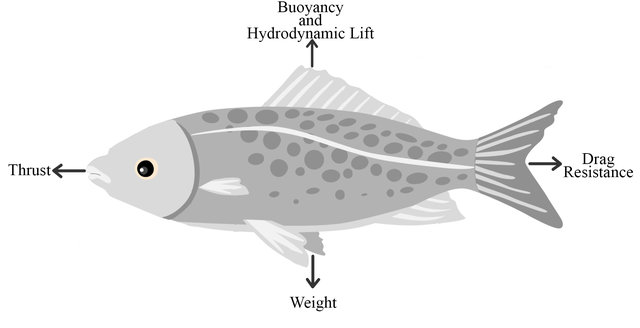
Underwater Soft Robotics: A Review of Bioinspiration in Design, Actuation, Modeling, and Control
Nature and biological creatures are some of the main sources of inspiration for humans. Engineers have aspired to emulate these natural systems. As rigid systems become increasingly limited in their capabilities to perform complex tasks and adapt to their environment like living creatures, the need for soft systems has become more prominent due to the similar complex, compliant, and flexible characteristics they share with intelligent natural systems. This review provides an overview of the recent developments in the soft robotics field, with a focus on the underwater application frontier. ©
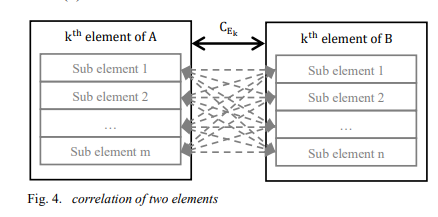
Systematic university decision making based on footprint identifiers
A new systematic decision-making framework for universities is presented. The framework avoids the disadvantages of the balanced score cards technique. A solid mathematical technique is provided for mapping processes and quality items. Application to the Egyptian system is fully explained. The footprint concept developed within an international initiative is introduced. The mathematical correlation algorithm main output is a decision matrix matching processes and quality aspects. Results illustrate automatic suitable matching between processes and quality standards. © 2021 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
