Breadcrumb
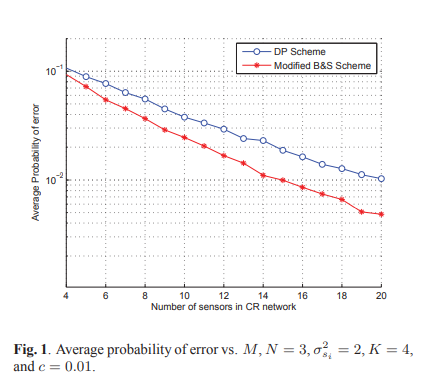
Cooperative sensing with sequential ordered transmissions to secondary fusion center
Successful spectrum sharing in a cognitive radio network depends on the correct and quick detection of primary activity. Cooperative spectrum sensing is therefore suggested to enhance the reliability of such detection. However, it renders another significant problem of increased detection delay and traffic burden. Moreover, efficient schemes for multi-sensor data fusion should be designed. In this paper, we employ sequential detection scheme together with ordered transmissions from cognitive detectors. We derive two sequential schemes, one that is capable of achieving the minimum probability
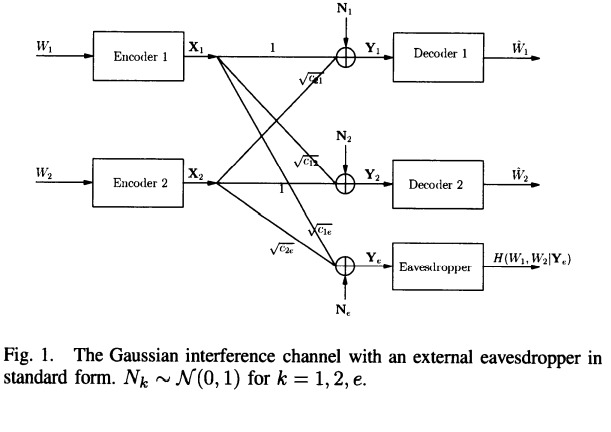
On the secrecy rate region for the interference channel
This paper studies interference channels with security constraints. The existence of an external eavesdropper in a two-user interference channel is assumed, where the network users would like to secure their messages from the external eavesdropper. The cooperative binning and channel prefixing scheme is proposed for this system model which allows users to cooperatively add randomness to the channel in order to degrade the observations of the external eavesdropper. This scheme allows users to add randomness to the channel in two ways: 1) Users cooperate in their design of the binning codebooks

On the flow anonymity problem in network coding
In this paper, we aim at protecting the privacy of the communicating parties while ensuring the authenticity of source nodes. In particular, we exploit intra-flow network coding to preserve the anonymity of communicating parties. Towards this objective, we propose an anonymity preservation scheme, namely closed group anonymity (CGA) that preserves the anonymity of the communicating parties via mixing their flows. Afterwards, we explore an instance of the Authentication-Privacy Trade-off in the context of Network Coding. We analyze the trade-off with the aid of the proposed anonymity scheme and
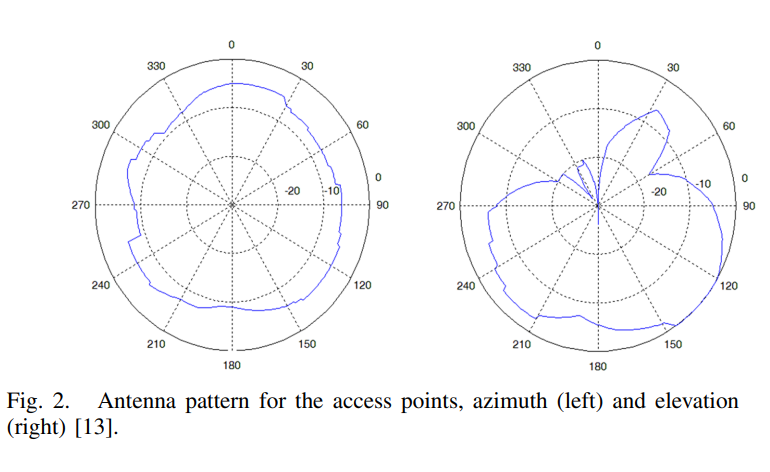

Propagation modeling for accurate indoor WLAN RSS-based localization
WLAN RSS-based localization has been a hot research topic for the last years. To obtain high accuracy in the noisy wireless channel, WLAN location determination systems usually use a calibration phase, where a radio map, capturing the signal strength signatures at different locations in the area of interest, is built. The radio map construction process takes a lot of time and effort, reducing the value of WLAN localization systems. In this paper, we propose 3D ray tracing as a way for automatically generating a highly accurate radiomap. We compare this method to previously used propagation
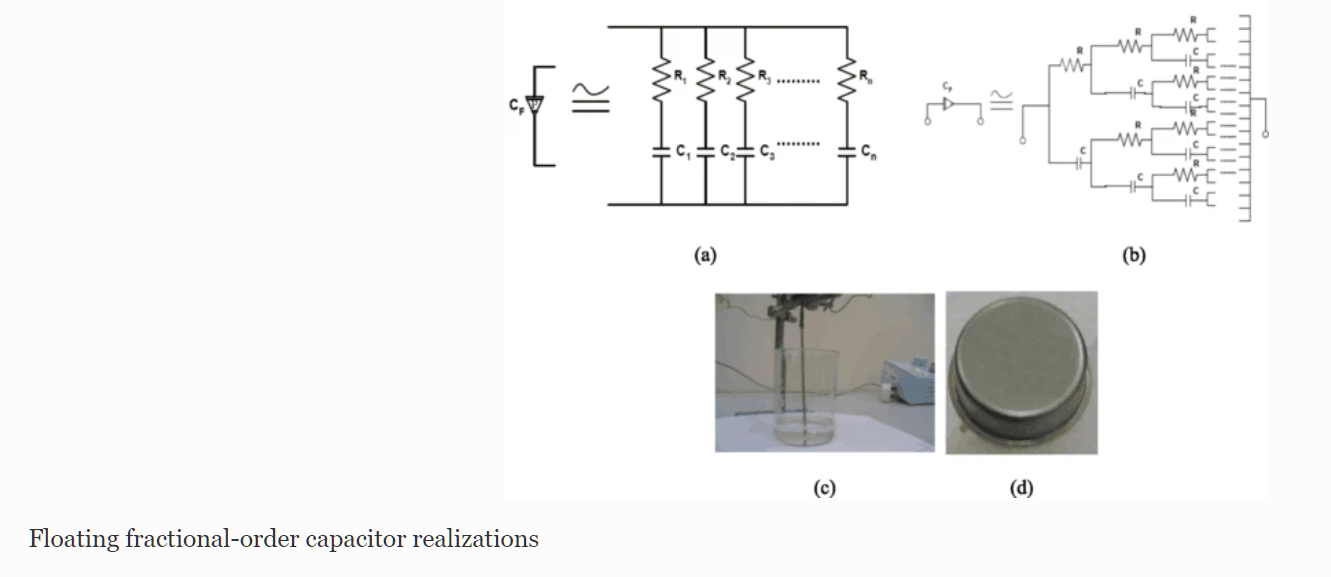
Optimization of fractional-order RLC filters
This paper introduces some generalized fundamentals for fractional-order RL β C α circuits as well as a gradient-based optimization technique in the frequency domain. One of the main advantages of the fractional-order design is that it increases the flexibility and degrees of freedom by means of the fractional parameters, which provide new fundamentals and can be used for better interpretation or best fit matching with experimental results. An analysis of the real and imaginary components, the magnitude and phase responses, and the sensitivity must be performed to obtain an optimal design
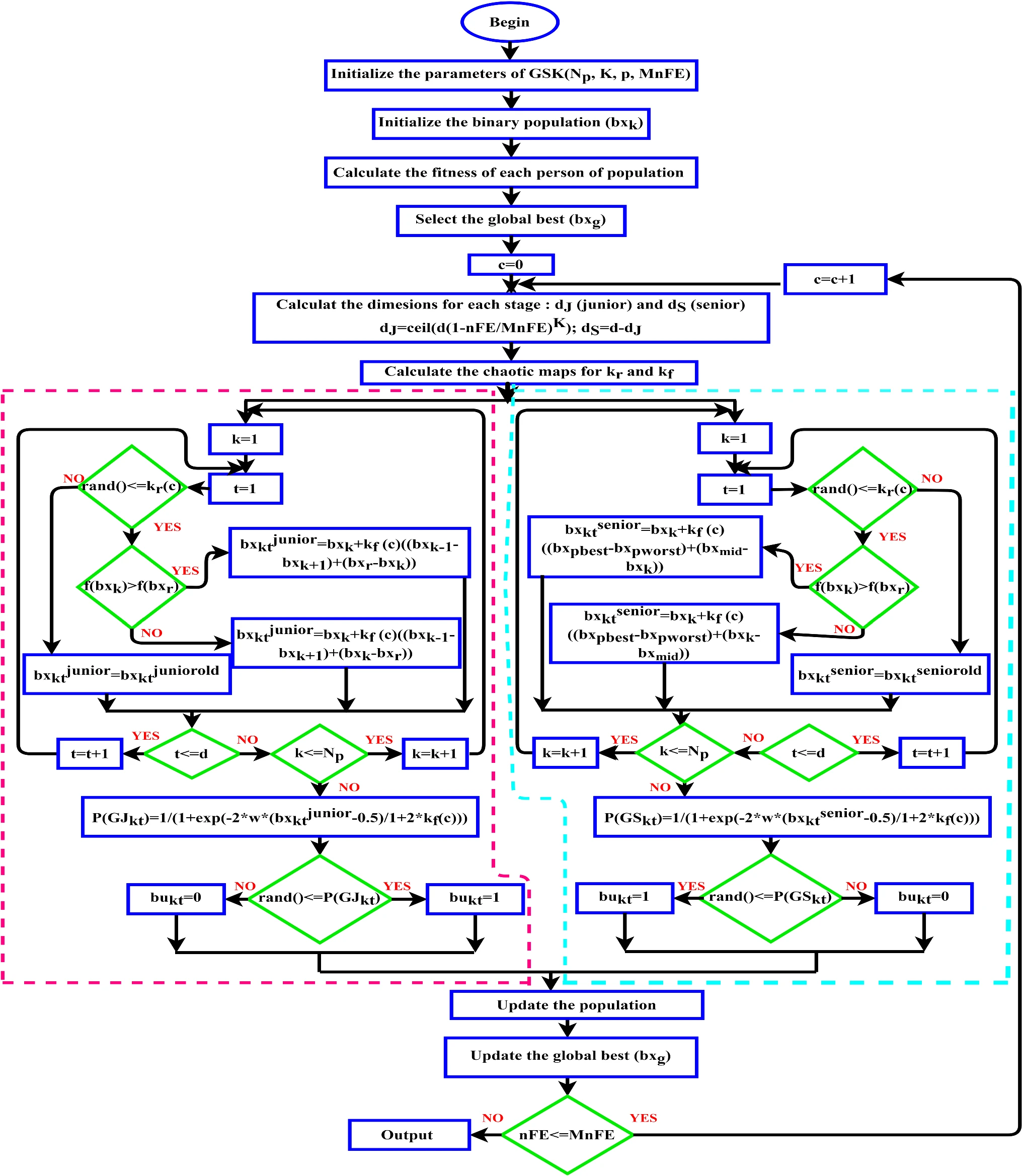
Chaotic gaining sharing knowledge-based optimization algorithm: an improved metaheuristic algorithm for feature selection
AROMA: Automatic generation of radio maps for localization systems
Current methods for building radio maps for wireless localization systems require a tedious, manual and error-prone calibration of the area of interest. Each time the layout of the environment is changed or different hardware is used, the whole process of location fingerprinting and constructing the radio map has to be repeated. The process gets more complicated in the case of localizing multiple entities in a device-free scenario, since the radio map needs to take all possible combinations of the location of the entities into account. In this demo, we present a novel system (AROMA) that is
Transmission power adaptation for cognitive radios
In cognitive radio (CR) networks, determining the optimal transmission power for the secondary users (SU) is crucial to achieving the goal of maximizing the secondary throughput while protecting the primary users (PU) from service disruption and interference. In this paper, we propose an adaptive transmission power scheme for cognitive terminals opportunistically accessing a primary channel. The PU operates over the channel in an unslotted manner switching activity at random times. The secondary transmitter (STx) adapts its transmission power according to its belief regarding the PU's state of
FPGA-Based Memristor Emulator Circuit for Binary Convolutional Neural Networks
Binary convolutional neural networks (BCNN) have been proposed in the literature for resource-constrained IoTs nodes and mobile computing devices. Such computing platforms have strict constraints on the power budget, system performance, processing and memory capabilities. Nonetheless, the platforms are still required to efficiently perform classification and matching tasks needed in various applications. The memristor device has shown promising results when utilized for in-memory computing architectures, due to its ability to perform storage and computation using the same physical element
Fractional Order Sliding Mode PID Controller/Observer for Continuous Nonlinear Switched Systems with PSO Parameter Tuning
In this article a fractional order sliding mode PID controller and observer for the stabilization of continuous nonlinear switched systems is proposed. The design of the controller and observer is done following the separation principle, this means that the observer and controller are designed in a separate fashion, so a hybrid controller is implemented by designing the sliding mode controller part using an integral sliding mode surface along with a PIλDμ controller part which is the fractional order PID controller that is implemented to stabilizes the system. For the observer part, an
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
