Breadcrumb
Implementation of PID Controller with PSO Tuning for Autonomous Vehicle
In the use of automatic control and its optimization methods, this research discusses how Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller is used to provide a smooth auto-parking for an electrical autonomous car. Different tuning methods are shown, discussed, and applied to the system looking forward to enhancing its performance. Time domain specifications are used as a criterion of comparison between tuning methods in order to select the best tuning method to the system with a proper cost function. Results show that Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method gives the best results according
Fractional-order bio-impedance modeling for interdisciplinary applications: A review
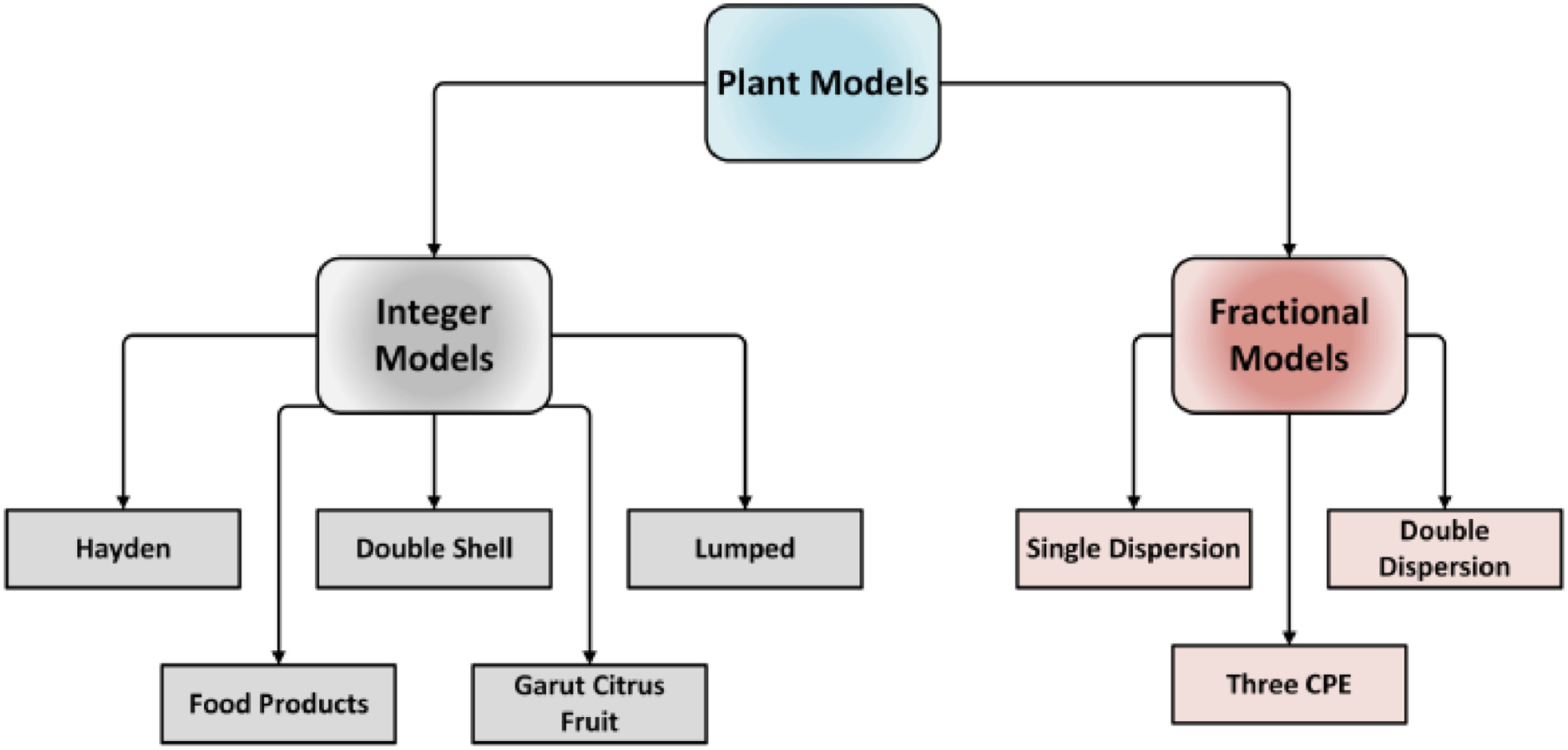
Bio-impedance circuit modeling is a popular and effective non-invasive technique used in medicine and biology to fit the measured spectral impedance data of living or non-living tissues. The variations in impedance magnitude and/or phase at different frequencies reflect implicit biophysical and biochemical changes. Bio-impedance is also used for sensing environmental changes and its use in the agriculture industry is rapidly increasing. In this paper, we review and compare among the fractional-order circuit models that best fit bio-impedance data and the different methods for identifying the
Memristive Bio-Impedance Modeling of Fruits and Vegetables
Recent works show that the plants can exhibit nonlinear memristive behavior when excited with low-frequency signals. However, in the literature, only linear bio-impedance models are extensively considered to model the electrical properties of biological tissues without acknowledging the nonlinear behavior. In this paper, we show with experiments, for the first time, the pinched hysteresis behavior in seven fruits and vegetables including tomato, orange, lemon, aubergine, and kiwi which exhibit single pinch-off point, and others such as carrot and cucumber exhibit double pinch-off points (i.e

Investigation of properties limiting efficiency in Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
We have investigated different nonidealities in Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with 9.7% conversion efficiency, in order to determine what is limiting the efficiency of these devices. Several nonidealities could be observed. A barrier of about 300 meV is present for electron flow at the absorber-buffer heterojunction leading to a strong crossover behavior between dark and illuminated current-voltage curves. In addition, a barrier of about 130 meV is present at the Mo-absorber contact, which could be reduced to 15 meV by inclusion of a TiN interlayer. Admittance spectroscopy results on the
Hierarchical proactive caching for vehicular ad hoc networks
Recently, emerging vehicular applications are increasing the demand of vehicles which form significant burdens on network backhaul and represents a cause to the quality of experience (QoE) decay of the vehicular users. Proactive caching is a promising technique to mitigate the load on core networks by caching some of the expected data items. This work proposes a hierarchical proactive caching scheme which jointly considers caching in vehicles and roadside units (RSUs). Minimization of the vehicle communication latency is the main objective of our study. The optimization problem is formulated
Cole-Cole Bio-Impedance Parameters Extraction from a Single Time-Domain Measurement
We show that the four parameters of a single-dispersion Cole-Cole bio-impedance model can be extracted from an one time-domain measurement with a fixed frequency. In particular, a periodic triangle waveform current excitation signal is injected into the biological sample under study while measuring the voltage developed across this sample in a galvanostatic measurement setup. The voltage response due to this triangle-wave excitation is firstly analytically derived in closed form. After that the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) is applied to extract the unknown model parameters
Cole bio-impedance model variations in daucus carota sativus under heating and freezing conditions
This paper reports on the variations in the parameters of the single dispersion Cole bio-impedance model of Daucus Carota Sativus (carrots) under heating and freezing conditions. Experiments are conducted on six samples with recorded live bio-impedance spectra versus temperature. The Cole model parameters are extracted from the measured data using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA) optimization technique and their variations are correlated with well-known bio-chemical and bio-mechanical variations. This represents a non-invasive method for characterizing and measuring the degree of change
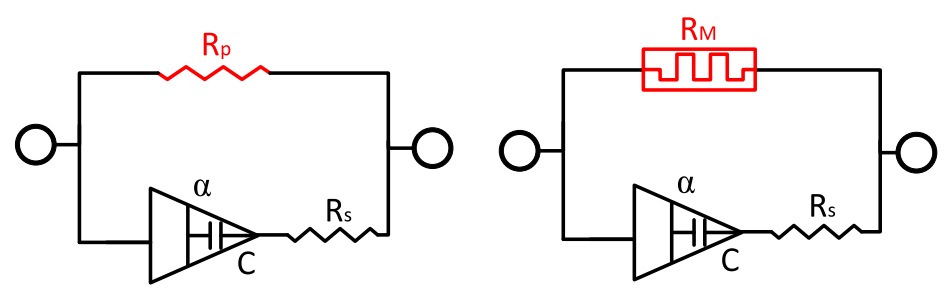
Experimental investigation of innovative active packaging biofilms using electrical impedance spectroscopy
Extending the double-dispersion Cole–Cole, Cole–Davidson and Havriliak–Negami electrochemical impedance spectroscopy models
Double-dispersion impedance models are important for the accurate fitting of spectral impedance measurements in Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). While the Cole–Cole model is the most widely known, it is possible to define double-dispersion Cole–Davidson and Havriliak–Negami models as well. In this work, we show that more freedom can be exercised when these three models are combined together and that this combination can be done in various forms. Experimental results using a two-stage optimization algorithm applied on the suggested models are provided. © 2021, European Biophysical
Extraction of Phase Information from Magnitude-Only Bio-impedance Measurements Using a Modified Kramers–Kronig Transform
The need for portable and low-cost bio-impedance analyzers that can be deployed in field studies has significantly increased. Due to size and power constraints, reducing the hardware in these devices is crucial and most importantly is removing the need for direct phase measurement. In this paper a new magnitude-only technique based on modified Kramers–Kronig transforms is proposed and tested. Comparison with impedance measurements of fresh and aging tomato samples using a precise industry standard impedance analyzer is carried out and explained. Error and noise analysis of the proposed
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
