Breadcrumb
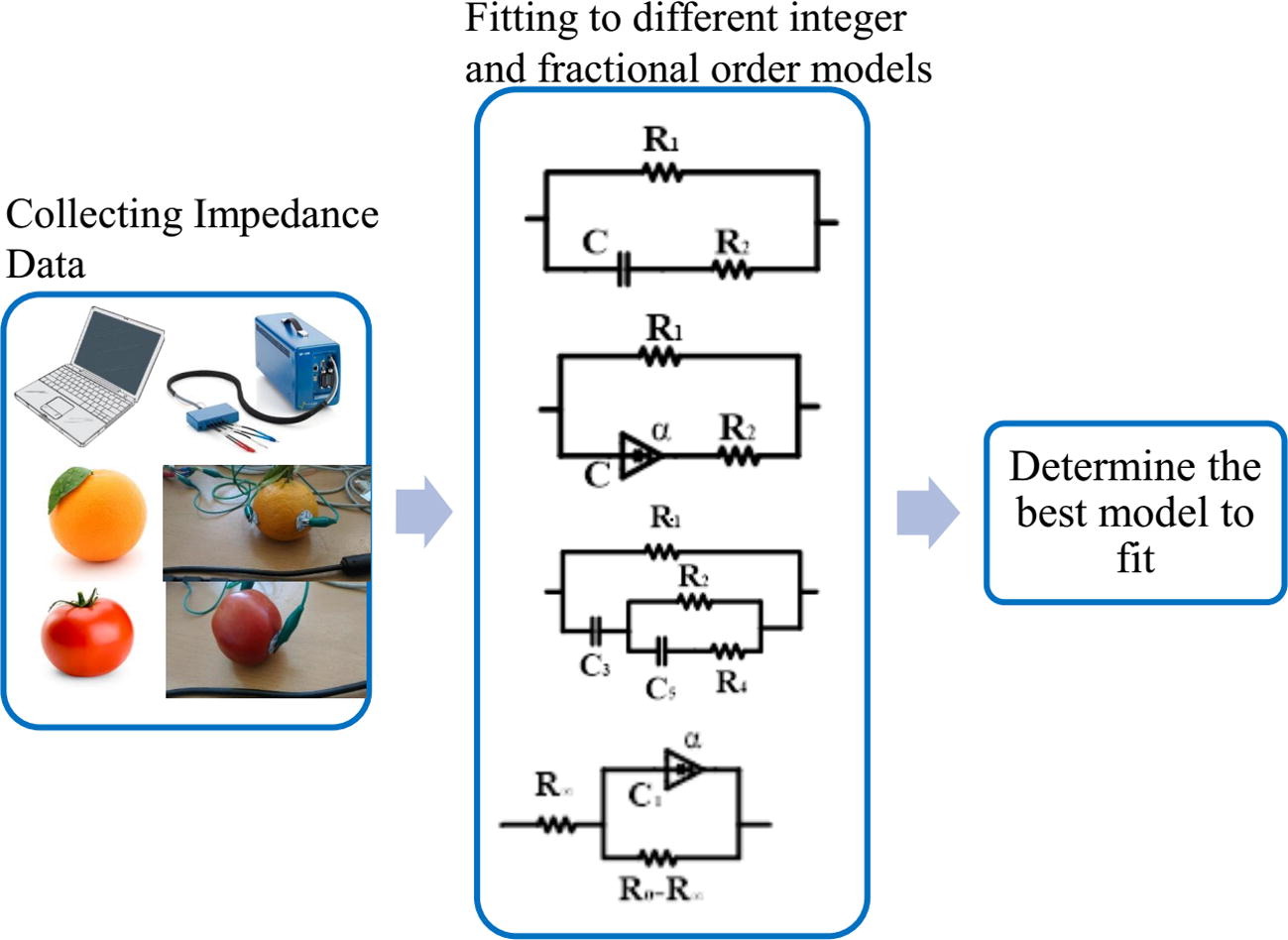
Experimental comparison of integer/fractional-order electrical models of plant
Extraction of bioimpedance phase information from its magnitude using a non-uniform Kramers–Kronig transform
A novel non-uniform Kramers–Kronig Transform algorithm for bioimpedance phase extraction is proposed and tested in this work. The algorithm error is studied and compared with a previously proposed phase extraction technique, also based on the Kramers–Kronig transform. Results using simulated datasets and experimental datasets confirm the excellent performance of the algorithm. © 2020, European Biophysical Societies' Association.
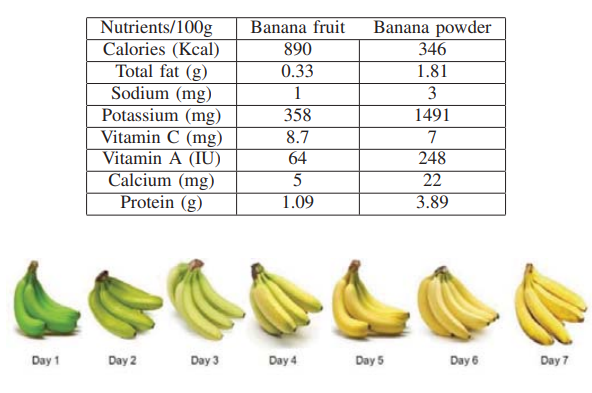
Banana ripening and corresponding variations in bio-impedance and glucose levels
This paper studies banana fruit ripping using the Cole-impedance model fitted over the measured bio-impedance data by monitoring the changes in the model parameters during the different ripping stages. A set of twenty bananas are tested for 84 hours, and impedance measurements are done every 12 hours using an SP150 electrochemical station. The changes in model parameters are related to the physical changes in the fruit as well as with the glucose concentration, which increases with time. © 2019 IEEE.
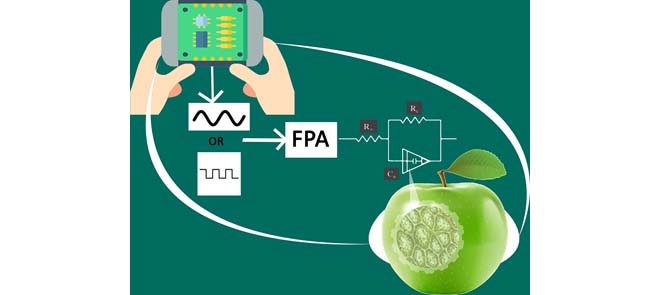
Extracting Optimized Bio-Impedance Model Parameters Using Different Topologies of Oscillators
This paper demonstrates the possibility of extracting the single-dispersion and double-dispersion Cole-bio-impedance model parameters using oscillators (sinusoidal or relaxation). The method is based on replacing selected components in the oscillator structure with the biological sample under test and then using the Flower Pollination optimization Algorithm (FPA) to solve a set of nonlinear equations in order to extract the unknown model parameters. Minimum component sinusoidal oscillators and relaxation oscillators are used in this work and experimental results on three samples of four
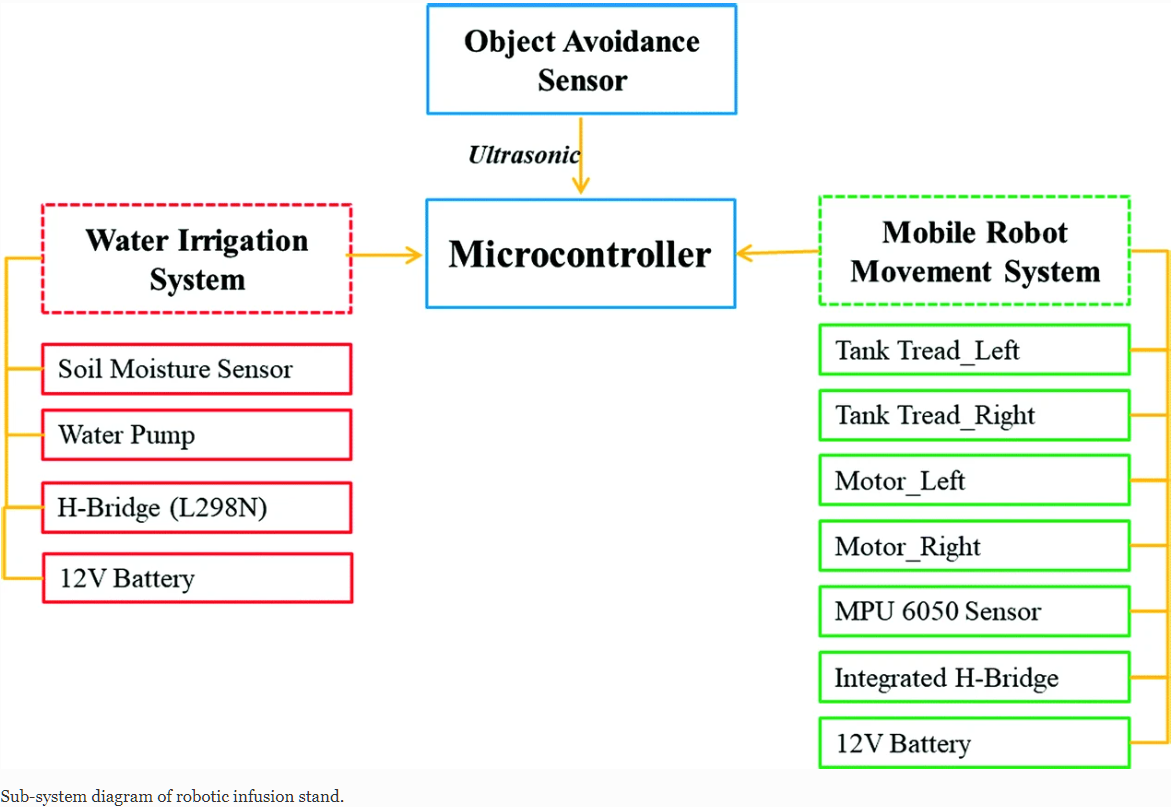
Optimal Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) Controller Design for Smart Irrigation Mobile Robot with Soil Moisture Sensor
Uncertainty on the condition of the weather always give a major headache to the agricultural industry as the cultivated plant that is grown on a large scale commercially rely on the condition of the weather. Therefore, to reduce the interdependency on the weather itself, a recommendation to develop a prototypic mobile robot for smart irrigation is submitted. Smart irrigation system is an essential tool from yield point of view and scarcity of the water. This smart irrigation system adopts a soil moisture sensor to measure the moisture content of the soil and automatically provide a signal to
Towards evolving sensor actor networks
Sensor Actor NETworks (SANET) represent a major component of ubiquitous service environments promising interesting solutions to a wide range of problems. Despite the obvious increase in the research activities proposing architectures and protocols for SANETs, we are still no where near the production of industrial-grade SANET software that can be relied upon for mission critical applications. The cost of programming, deploying and maintaining SANET environments is still highly prohibitive due to the lack of industrial tools capable of realizing adaptive SANET software in a cost effective way
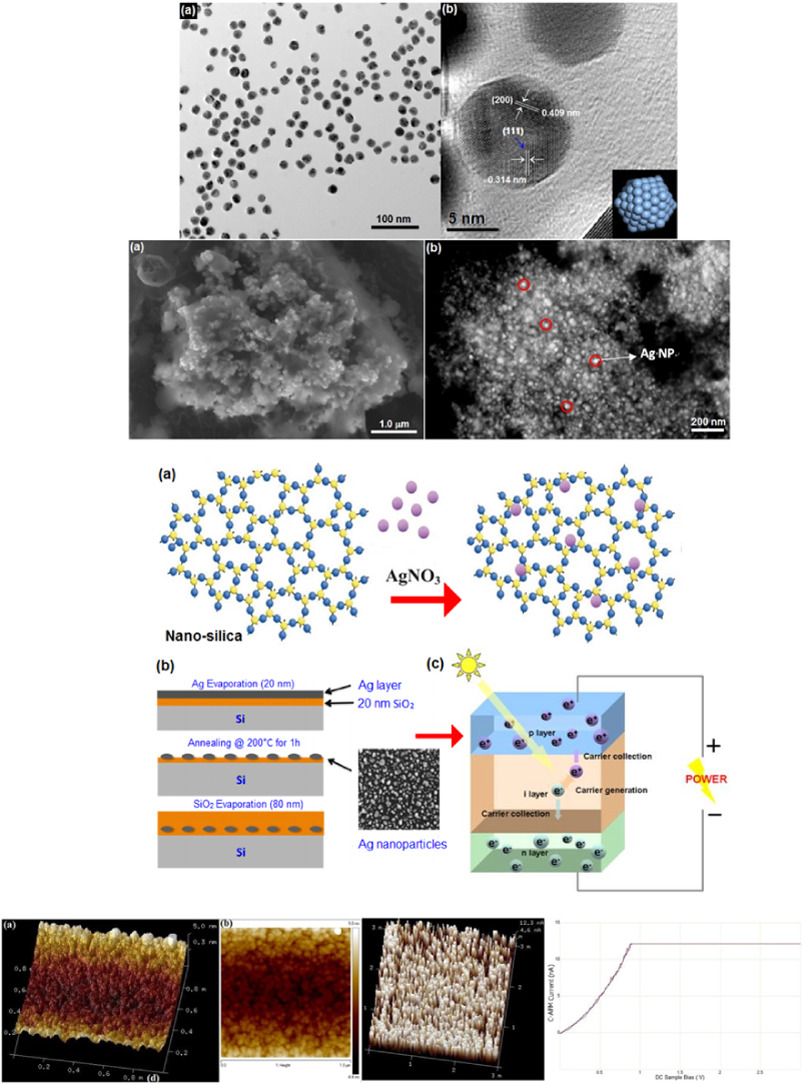
Aggrandize efficiency of ultra-thin silicon solar cell via topical clustering of silver nanoparticles
A highly efficient photovoltaic nanocomposite device is demonstrated by fabrication of structural clusters of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) on silicon solar cells via a boil deposition method. The efficiency of silicon solar cell was augmented by coating Ag NPs ultra-thin-film deposition on silicon solar cell. Chemically synthesized silver NP's, their consumption on a silicon thin layer and the operation of photovoltaic nanocomposite device were characterized by using several electron probe microscopic pectroscopic and spectrometric techniques viz. x-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron
Study of Energy Harvesters for Wearable Devices
Energy harvesting was and still an important point of research. Batteries have been utilized for a long time, but they are now not compatible with the downsizing of technology. Also, their need to be recharged and changed periodically is not very desirable, therefore over the years energy harvesting from the environment and the human body have been investigated. Three energy harvesting methods which are the Piezoelectric energy harvesters, the Enzymatic Biofuel cells, and Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are being discussed in the paper. Although Biofuel cells have been investigated for a
Study of fractional flux-controlled memristor emulator connections
In this paper, the series and parallel connections of the fractional flux-controlled memristors are studied. Asymmetric I-V hysteresis with high I-V nonlinearity can be obtained from single fractional memristor as reported in literature. However, connecting different memristor emulators can convert the asymmetric hysteresis to symmetric one and maintaining the high I-V nonlinearity to be used in some memristor devices. The proposed circuits have been analyzed mathematically to study the effect of changing the frequency and fractional power. Different cases have been verified on PSpice using
Stochastic modeling of mushroom—waveguide photodetectors
Waveguide photodetectors (WGPDs) are one of the promising candidates to solve the tradeoff between the quantum efficiency and the transit time in the surface illuminated photodiodes where the lightwave is incident laterally perpendicular to the direction of the flow of generated carriers, enhancing both high speed and quantum efficiency. In Mushroom-WGPDs, the performance degradation due its parasitic capacitance and the load resistance is overcome due to the mesa mushroom structure. Inaccuracies in the dimensions of’Mushroom-WGPDs due to the fabrication affect its functionality and its
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
