Breadcrumb
Parameter Estimation of Two Spiking Neuron Models With Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms
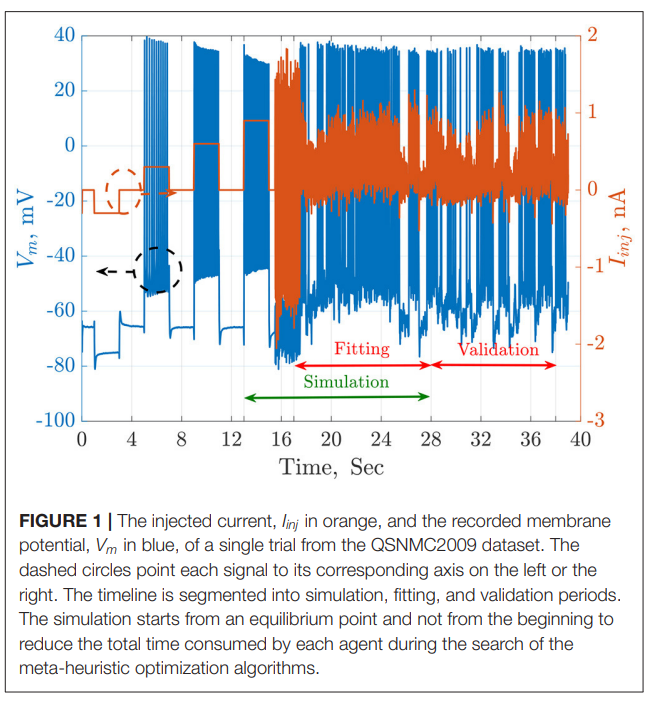
The automatic fitting of spiking neuron models to experimental data is a challenging problem. The integrate and fire model and Hodgkin–Huxley (HH) models represent the two complexity extremes of spiking neural models. Between these two extremes lies two and three differential-equation-based models. In this work, we investigate the problem of parameter estimation of two simple neuron models with a sharp reset in order to fit the spike timing of electro-physiological recordings based on two problem formulations. Five optimization algorithms are investigated; three of them have not been used to
A fuzzy approach of sensitivity for multiple colonies on ant colony optimization
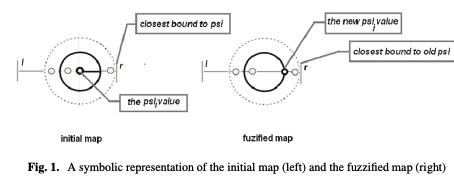
In order to solve combinatorial optimization problem are used mainly hybrid heuristics. Inspired from nature, both genetic and ant colony algorithms could be used in a hybrid model by using their benefits. The paper introduces a new model of Ant Colony Optimization using multiple colonies with different level of sensitivity to the ant’s pheromone. The colonies react different to the changing environment, based on their level of sensitivity and thus the exploration of the solution space is extended. Several discussion follows about the fuzziness degree of sensitivity and its influence on the
Gesture recognition for improved user experience in augmented biology lab
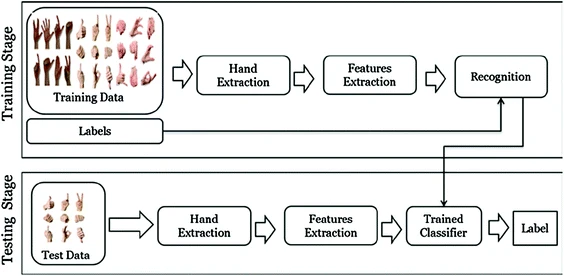
The Learning process in education systems is one of the most important issues that affect all societies. Advances in technology have influenced how people communicate and learn. Gaming Techniques (GT) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies provide new opportunities for a learning process. They transform the student’s role from passive to active in the learning process. It can provide a realistic, authentic, engaging and interesting learning environment. Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) is a major driver in the field of Augmented Reality (AR). In this paper, we propose an initiative Augmented
Finite element analysis of pulsatile blood flow in elastic artery
New hybrid Eulerian/Lagrangian model is presented accounting for the two-way coupling between the pulsating blood flow and the artery deformability. The Streamline-Upwind/Petrove--Galerkin (SUPG) finite element technique is used to treat for the convective nature of the momentum equation. The deformability of the artery walls is accounted for by treating the wall as an elastic beam under transverse unsteady distributed load, namely the fluid pressure. The results of the present contribution compare well against the available published data. © 2019, Isfahan University of Technology.
Fine tuning the enhanced suffix array
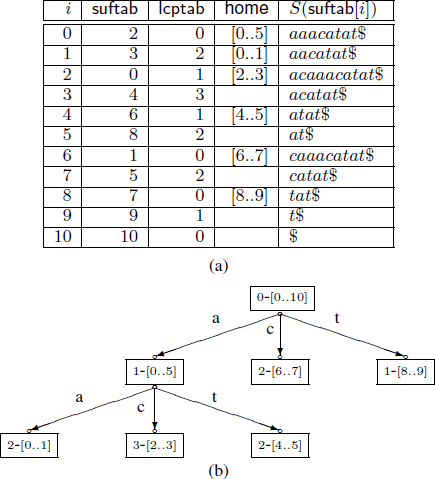
The enhanced suffix array is an indexing data structure used for a wide range of applications in Bioinformatics. It is basically the suffix array but enhanced with extra tables that provide extra information to improve the performance in theory and in practice. In this paper, we present a number of improvements to the enhanced suffix array: 1) We show how to find a pattern of length m in O(m) time, i.e., independent of the alphabet size. 2) We present an improved representation of the bucket table. 3) We improve the access time of addressing the LCP (longest common prefix) table when one byte
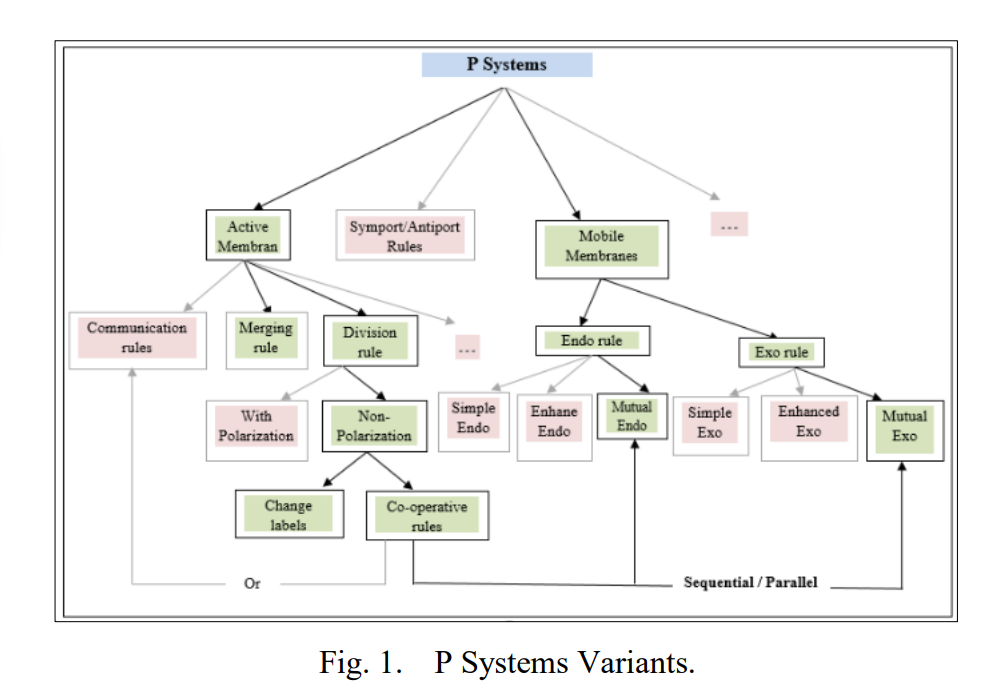
P Systems Implementation: A Model of Computing for Biological Mitochondrial Rules using Object Oriented Programming
Membrane computing is a computational framework that depends on the behavior and structure of living cells. P systems are arising from the biological processes which occur in the living cells’ organelles in a non-deterministic and maximally parallel manner. This paper aims to build a powerful computational model that combines the rules of active and mobile membranes, called Mutual Dynamic Membranes (MDM). The proposed model will describe the biological mechanisms of the metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics made by mitochondrial membranes. The behaviors of the proposed model regulate
Detection of cardiac function abnormality from MRI images using normalized wall thickness temporal patterns
Purpose. To develop a method for identifying abnormal myocardial function based on studying the normalized wall motion pattern during the cardiac cycle. Methods. The temporal pattern of the normalized myocardial wall thickness is used as a feature vector to assess the cardiac wall motion abnormality. Principal component analysis is used to reduce the feature dimensionality and the maximum likelihood method is used to differentiate between normal and abnormal features. The proposed method was applied on a dataset of 27 cases from normal subjects and patients. Results. The developed method
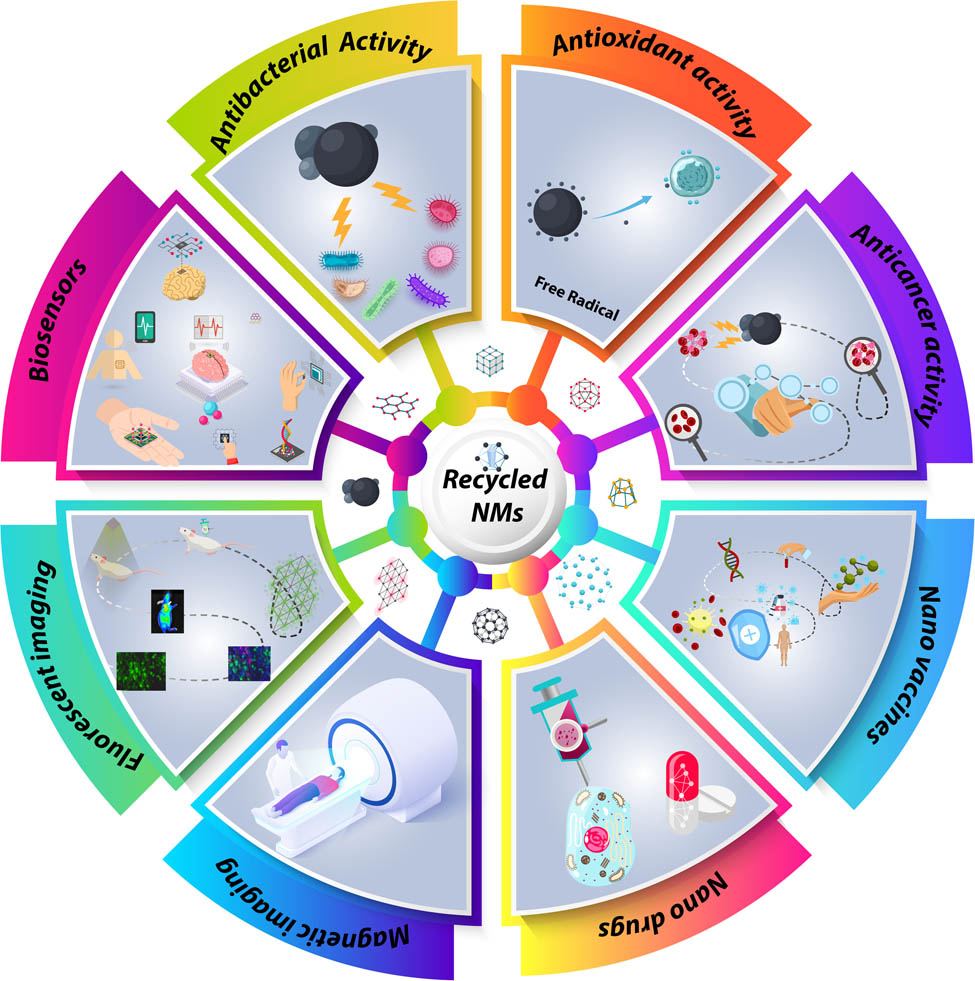
Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
Global overpopulation, industrial expansion, and urbanization have generated massive amounts of wastes. This is considered as a significant worldwide challenge that requires an urgent solution. Additionally, remarkable advances in the field of biomedicine have impacted the entire spectrum of healthcare and medicine. This has paved the way for further refining of the outcomes of biomedical strategies toward early detection and treatment of different diseases. Various nanomaterials (NMs) have been dedicated to different biomedical applications including drug delivery, vaccinations, imaging
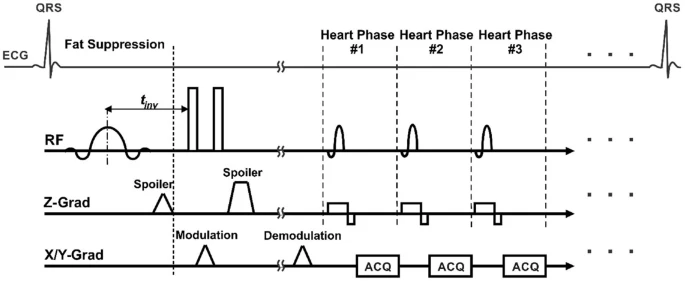
An efficient fat suppression technique for stimulated-echo based CMR
[No abstract available]
Comparative 16S Metabarcoding of Nile Tilapia Gut Microbiota from the Northern Lakes of Egypt
Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, is the principal fish bred in Egypt. A pilot study was designed to analyze the bacterial composition of the Nile tilapia fish guts from two saltwater lakes in Northern Egypt. Fish samples were obtained from two Delta lakes: Manzala (ML) and Borollus (BL). DNA was extracted, and the bacterial communities in the stomach content were classified (down to the species level) using the 16S rRNA-based analysis. From the two metagenomics libraries in this study, 1,426,740 reads of the amplicon sequence corresponding to 508 total taxonomic operational units were
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
