Breadcrumb
Error analysis of fundus image registration using quadratic model transfformation
Based registration of retinal images proved to be very successful especially for minimally overlapping images. The most commonly used transformation method uses a quadratic model to represent the geometry of the retinal surface. Although this model has been used for more than one decade, there is no literature that studies the model errors for abnormal eye geometries. In this work, we present a study of the registration errors of the quadratic model in case of diseased eyes. The study includes two basic models of the retinal surface for eyes suffering from: myopia; and retinal diseases (e.g
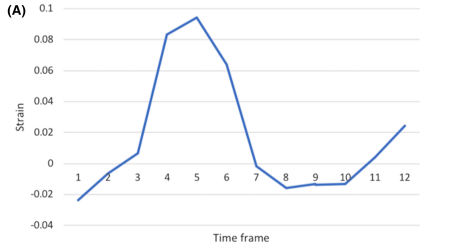
Detecting liver fibrosis using a machine learning-based approach to the quantification of the heart-induced deformation in tagged MR images
Liver disease causes millions of deaths per year worldwide, and approximately half of these cases are due to cirrhosis, which is an advanced stage of liver fibrosis that can be accompanied by liver failure and portal hypertension. Early detection of liver fibrosis helps in improving its treatment and prevents its progression to cirrhosis. In this work, we present a novel noninvasive method to detect liver fibrosis from tagged MRI images using a machine learning-based approach. Specifically, coronal and sagittal tagged MRI imaging are analyzed separately to capture cardiac-induced deformation
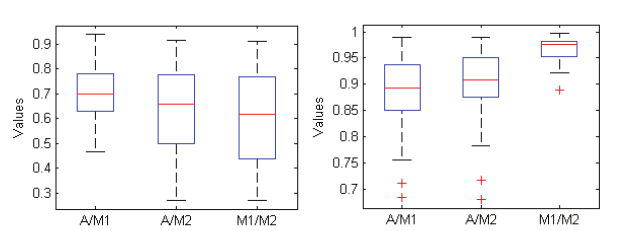
Segmentation of Diabetic Macular Edema in fluorescein angiograms
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FA) is a powerful tool for imaging and evaluating Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), where the fluorescein dye leaks and accumulates in the diseased areas. Currently, the assessment of FA images is qualitative and suffers from large inter-observer variability. A necessary step towards quantitative assessment of DME is automatic segmentation of fluorescein leakage. In this work, we present an automatic method for segmenting DME areas in FA images. The method is based on modeling the macular image in the early time frame using 2D Gaussian surfaces, which is then
Comparison of Machine Learning Approaches for Prediction of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients
Background/Aim: Using machine learning approaches as non-invasive methods have been used recently as an alternative method in staging chronic liver diseases for avoiding the drawbacks of biopsy. This study aims to evaluate different machine learning techniques in prediction of advanced fibrosis by combining the serum bio-markers and clinical information to develop the classification models. Methods: A prospective cohort of 39,567 patients with chronic hepatitis C was divided into two sets - one categorized as mild to moderate fibrosis (F0-F2), and the other categorized as advanced fibrosis (F3
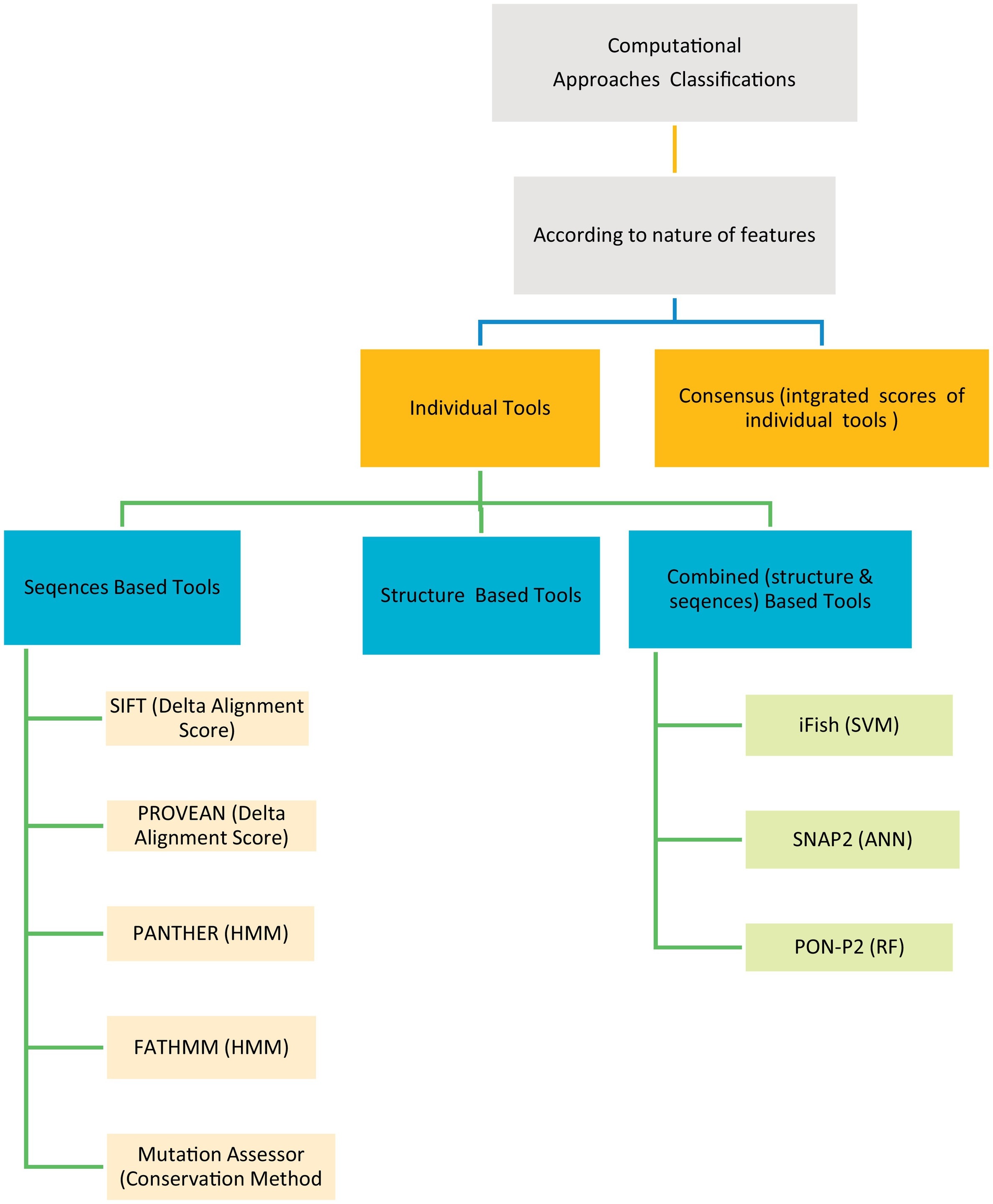
Evaluation of computational techniques for predicting non-synonymous single nucleotide variants pathogenicity
The human genetic diseases associated with many factors, one of these factors is the non-synonymous Single Nucleotide Variants (nsSNVs) cause single amino acid change with another resulting in protein function change leading to disease. Many computational techniques have been released to expect the impacts of amino acid alteration on protein function and classify mutations as pathogenic or neutral. Here in this article, we assessed the performance of eight techniques; FATHMM, SIFT, Provean, iFish, Mutation Assessor, PANTHER, SNAP2, and PON- P2 using a VaribenchSelectedPure dataset of 2144
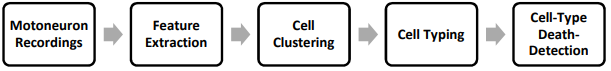
Automated Cell-Type Classification and Death-Detection of Spinal Motoneurons
Spinal motoneurons (MNs) play a crucial role in movement control. Decoding the firing activity of spinal MNs could help in real-life challenges, such as enhancing the control of myoelectric prostheses and diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. In this paper, we propose a machine learning approach to automatically classify MNs based on their firing activity. Applying the proposed approach to data from a MN computational model, the classification accuracy of all examined datasets exceeded 95%. We extended the approach to detecting the death of a given MN type using clustering validity index
Segmentation of Choroidal Neovascularization lesions in fluorescein angiograms using parametric modeling of the intensity variation
Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) is a severe retinal disease characterized by abnormal growth of blood vessels in the choroidal layer. Current diagnosis of CNV depends mainly on qualitative assessment of a temporal sequence of fundus fluorescein angiography images. Automated segmentation and identification of the CNV lesion types (either occult or classic) is required to reduce the inter-and intra- observer variability and also to reduce the manual segmentation effort and time. In this work, we present automatic segmentation method for the CNV lesions. The method is based on developing a
Segmentation of choroidal neovascularization in fundus fluorescein angiograms
Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is a common manifestation of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). It is characterized by the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the choroidal layer causing blurring and deterioration of the vision. In late stages, these abnormal vessels can rupture the retinal layers causing complete loss of vision at the affected regions. Determining the CNV size and type in fluorescein angiograms is required for proper treatment and prognosis of the disease. Computer-aided methods for CNV segmentation is needed not only to reduce the burden of manual segmentation but
Detection of Mammalian Coding Sequences Using a Hybrid Approach of Chaos Game Representation and Machine Learning
Mammalian protein-coding sequence detection provides a wide range of applications in biodiversity research, evolutionary studies, and understanding of genomic features. Representation of genomic sequences in Chaos Game Representation (CGR) helps reveal hidden features in DNA sequences due to its ability to represent sequences in both numerical and graphical levels. Machine learning approaches can automatically detect hidden patterns in CGR images by detecting and classifying protein-coding and noncoding patterns accurately. Here, we propose a pipeline that automatically detects coding (exons)
Classification of cardiac magnetic resonance image type and orientation
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging provides a number of different imaging acquisition types and views of different body cross sections and orientations. A huge amount of images are produced which demand an automatic method for classification based on the visual contents to facilitate diagnosis and searching operations. In this work, we propose a fully automated classification method for classifying cardiac MRI images according to image acquisition type and orientation. Local binary pattern is used to represent the texture differences among the different image types. Edge orientation histogram
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
