Breadcrumb
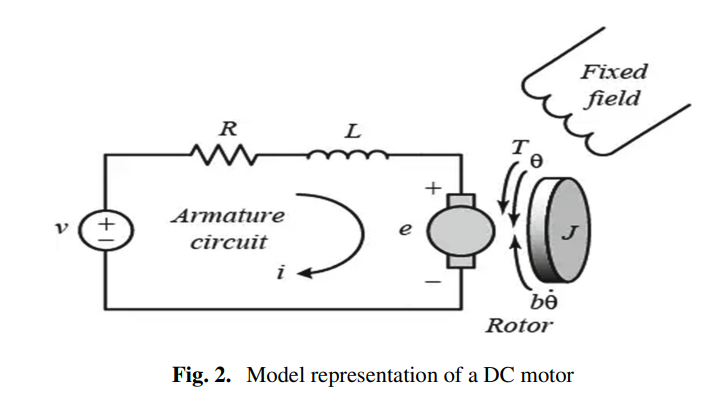
Fuzzy Logic Controller with Color Vision System Tracking for Mobile Manipulator Robot
The purpose of this article is to present a theoretical and practical implementation of a fuzzy algorithm methodology to control a mobile manipulator path planning using a real-time vision system tracking. To meet high performance response and robust stability of the platform navigation, a fuzzy logic controller is designed with realistic constrains. OpenCV library is used to implement Background Modeling technique to track in real time a color object and to extract its (X, Z) coordinates, then an ultrasonic sensor is coupled with the camera to calculate the depth “Y” of the tracked object
Solving Inverse Kinematics of a 7-DOF Manipulator Using Convolutional Neural Network
This paper presents a way to solve inverse kinematics of a 7-DOF manipulator using artificial neural networks. The manipulator consists of a 6-DOF articulated arm installed on a linear guide system to increase the workspace of the robot. The purpose of this paper is to provide an alternative to the traditional and complicated way to solve inverse kinematics by using artificial neural networks. The training data is generated from MATLAB after obtaining the DH parameters and workspace of the manipulator. Then, it was fed to the convolutional neural architecture to obtain a model for the

Design, simulation, and kinematics of 9-DOF Serial-Parallel Hybrid Manipulator Robot
Serial manipulator robot is one of the most advanced robots in the last decade. The demand for this type of robot leads the researchers to develop and improve the robot to increase its workspace, speed and to minimize the control complexity. This paper presents a novel robot configuration that combines a 6 DOF serial manipulator with a 3 DOF spherical parallel wrist. The serial manipulator is KUKA kr6 R900 type, which is a real industrial robot. At the same time, the parallel spherical wrist is 3-RRS type (Revolute- Revolute-Spherical Joint), which can support one translation movement in the Z
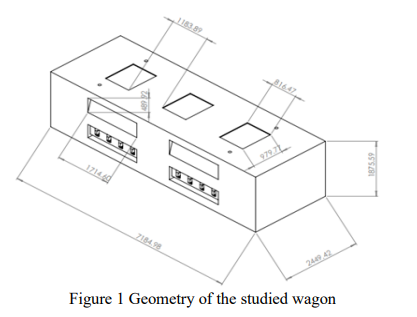
Regression Modeling for the Ventilation Effect on COVID-19 Spreading in Metro Wagons
The effect of different ventilation parameters on the infection potential of COVID-19 in a metro wagon is numerically studied. Two key indicators are used to quantify this potential. Based on the numerical results a regression analysis is performed to come up with the most suitable regression model for these key parameters. The proposed regression models are helpful in quantifying the infection risk at different ventilation scenarios. © 2021 IEEE.

Two-wheeled Self balancing robot Modeling and Control using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
This paper is focusing on the problem of the Self balancing robot which has many potentials due to its power consumption and maneuverability advantages. Modelling and controlling of the two-wheeled self-balancing robot is presented. For modelling part, two models were used in compare with a real proposed robot. At first, mathematical model was driven and the state space was achieved to model the plant of the system. Second, Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous (NARX) Neural Network model is introduced using recorded data architecture-based as it is used in time-series modeling for many reported
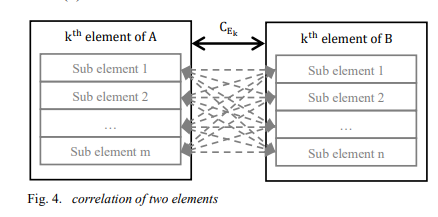
Systematic university decision making based on footprint identifiers
A new systematic decision-making framework for universities is presented. The framework avoids the disadvantages of the balanced score cards technique. A solid mathematical technique is provided for mapping processes and quality items. Application to the Egyptian system is fully explained. The footprint concept developed within an international initiative is introduced. The mathematical correlation algorithm main output is a decision matrix matching processes and quality aspects. Results illustrate automatic suitable matching between processes and quality standards. © 2021 IEEE.
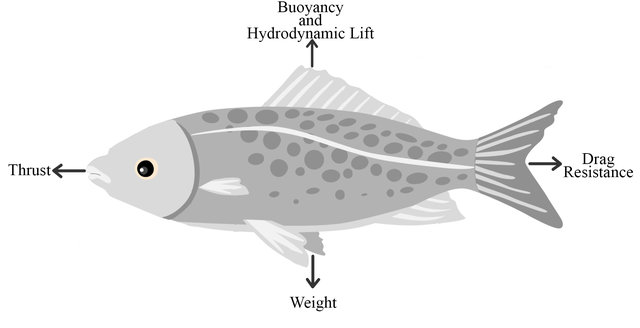
Underwater Soft Robotics: A Review of Bioinspiration in Design, Actuation, Modeling, and Control
Nature and biological creatures are some of the main sources of inspiration for humans. Engineers have aspired to emulate these natural systems. As rigid systems become increasingly limited in their capabilities to perform complex tasks and adapt to their environment like living creatures, the need for soft systems has become more prominent due to the similar complex, compliant, and flexible characteristics they share with intelligent natural systems. This review provides an overview of the recent developments in the soft robotics field, with a focus on the underwater application frontier. ©

Lid-Driven Cavity Flow with Elliptic Obstacle at Different Orientations
The aim of the present work is to predict the flow field around an elliptic obstacle at different orientations inside a square Lid-Driven Cavity (LDC). The Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) is used to simulate the flow at a Reynolds number, Re, of 100, using the two-dimensional nine-velocity, (D2Q9) lattice configuration and the BGK collision operator. The in-house code is validated using data from the literature for the case of LDC with a central circular cylinder. Different ellipse orientations are tested (0°, 30°, 45°, 90°, 120°, 145°, and 150°) to check the effect of orientation on the vortex
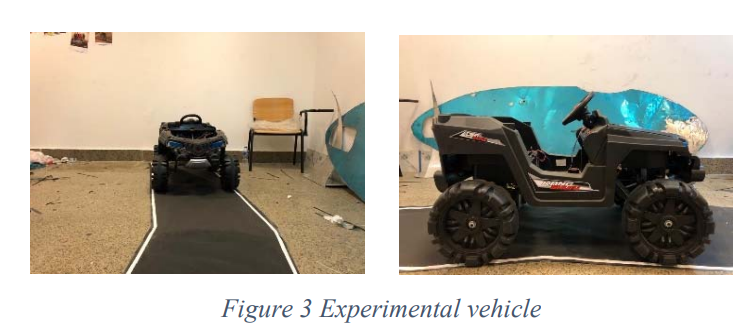
Steering Control for Autonomous Vehicles Using PID Control with Gradient Descent Tuning and Behavioral Cloning
In this paper we implement and evaluate two ways of controlling the steering angle of an autonomous vehicle, PID control with manual tuning followed by gradient descent algorithm tuning-which is able to enhance the performance through self-adjusting the controller parameters-and using supervised machine learning through the end-to-end deep learning for self-driving car which implement Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to predict the steering angle for a given instance of a track. The verification testing went through two phases: software simulation using python for first run testing and C++

Metaheuristic Optimization of Fractional Order Incremental Conductance (FO-INC) Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
This paper seeks to improve the photovoltaic (PV) system efficiency using metaheuristic, optimized fractional order incremental conductance (FO-INC) control. The proposed FO-INC controls the output voltage of the PV arrays to obtain maximum power point tracking (MPPT). Due to its simplicity and efficiency, the incremental conductance MPPT (INC-MPPT) is one of the most popular algorithms used in the PV scheme. However, owing to the nonlinearity and fractional order (FO) nature of both PV and DC-DC converters, the conventional INC algorithm provides a trade-off between monitoring velocity and
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
