Nonlinear single-input single-output model-based estimation of cardiac output for normal and depressed cases
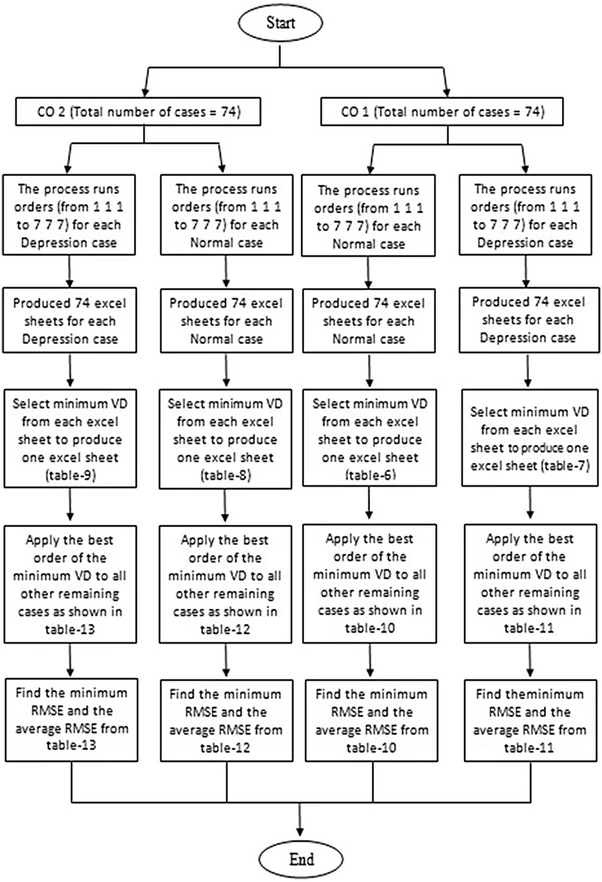
Mental depression is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality, thus provisioning generic simple nonlinear mathematical models for normal and depressed cases using only heart rate (HR) or stroke volume (SV) as a single input to produce cardiac output (CO) as a single output instead of using both HR and SV as two inputs. The proposed models could be in the future an effective tool to investigate the effect of neuroleptic medication, especially depression, and it reduces the time of processing. Seventy-four depressed cases, 74 normal peers and autoregressive considered as a main role in the nonlinear discrete system identification are chosen to lie under investigation on the way to produce four simple nonlinear models. The first generic model using only HR as an input which generated from the depressed case number 62 produced minimum root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 0.0018 and when it is applied to the 74 depressed cases it produced average RMSE equal to 0.1978. Second, generic model using only HR as an input created from the normal case number 55 produced minimum RMSE of 0.0008 and average RMSE equal to 0.0572. The third generic model using only SV as an input which generated from the depressed case number 16 produced minimum RMSE of 0.0027 and when it is applied to the 74 depressed cases it produced average RMSE equal to 0.9405. Fourth generic model using only SV as an input created from the normal case number 58 produced minimum RMSE of 0.0019 and average RMSE equal to 1.0833. The four simple nonlinear models for depression and normal cases are succeeded to determine CO by using only one input such as HR or SV and could be a good contribution in the future to neuroleptic medications field especially depression while HR showed the minimum average RMSE. © 2017, The Natural Computing Applications Forum.